Docker in Action
核心技术
Docker底层是基于成熟的Linux Container(LXC)技术实现。自Docker 0.9版本起,Docker除了继续支持LXC之外,还开始引入自家的runc,试图打造更通用的底层容器虚拟化库。
runc is a CLI tool for spawning and running containers according to the OCI specification.
从操作系统功能上看,Docker底层依赖的核心技术主要包括:
- Namespaces (Linux操作系统的命名空间)
- Control Groups (控制组)
- Union File Systems (联合文件系统,目前支持的联合文件系统种类包括,AUFS, btrfs, vfs和DeviceMapper等)
- Linux虚拟网络
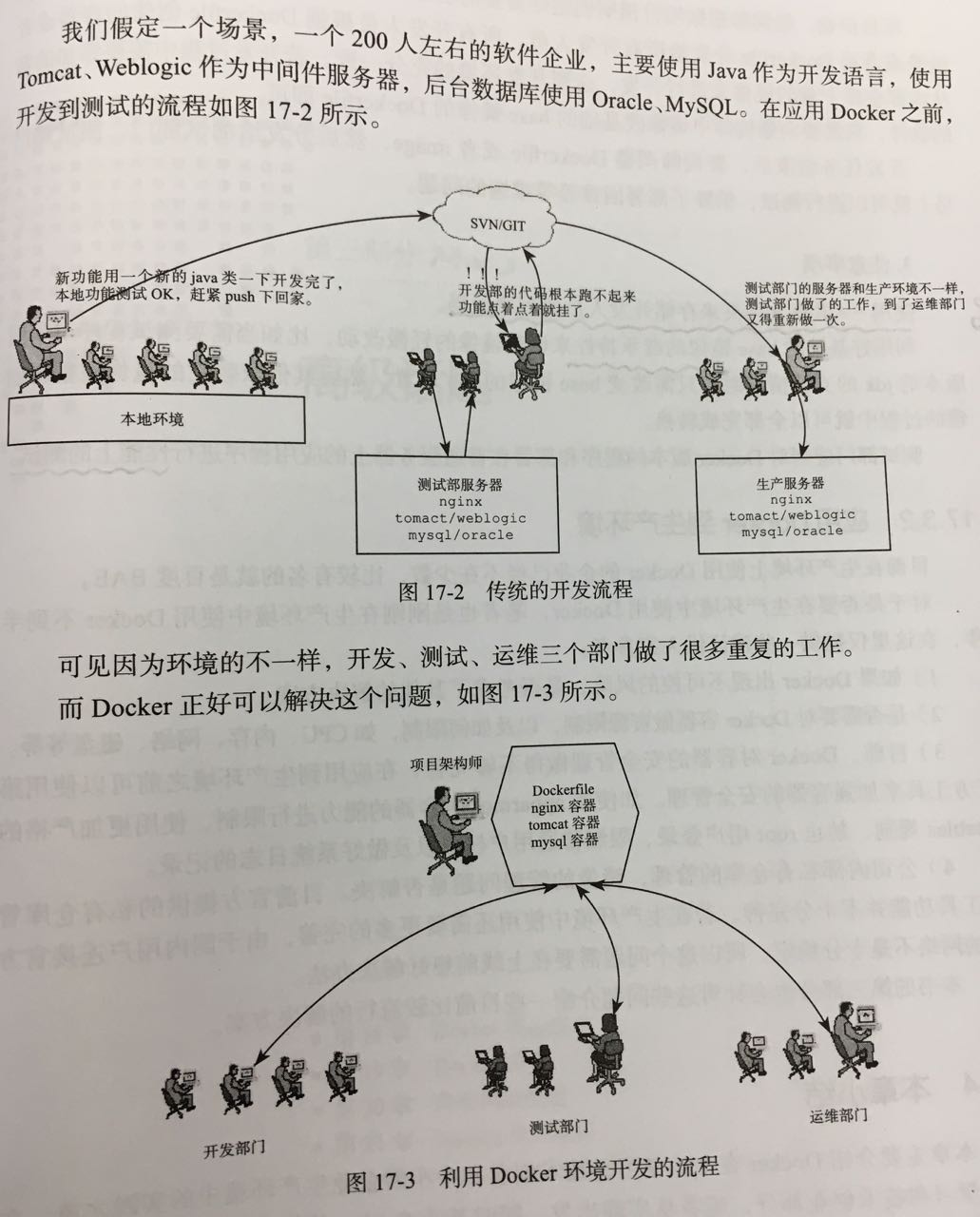
开发流程对比
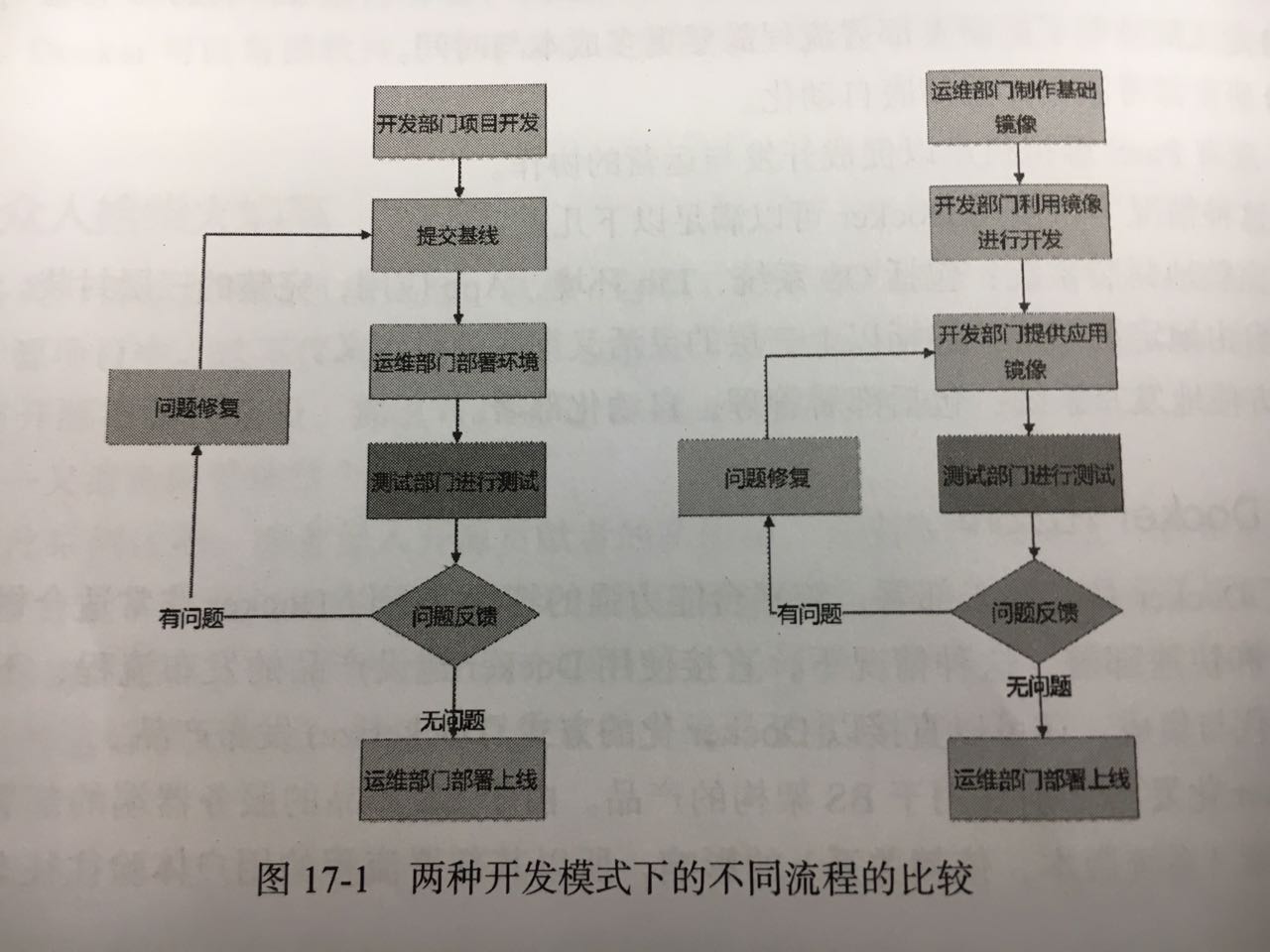
- 在Docker应用中,项目架构师的作用贯穿整个开发,测试,生产三个环节。
- 项目伊始,架构师根据项目预期创建好需要的基础Base镜像(比如,Nginx, Tomcat, MySQL等镜像),或者将Dockerfile分发给所有开发,所有开发根据Dockerfile创建的镜像来进行开发,达到开发环境充分一致。
- 若开发过程中需要添加新的程序,需要向架构师申请修改基础的Base镜像的Dockerfile。
- 开发完成后,将Dockerfile提交给测试,消除部署困难的问题。
- 使用
-v共享文件夹来存储开发的程序代码。 - 利用好Base镜像的继承特性来调整镜像的轻微改动。即,只需要修改Base镜像,而不需要修改其他依赖的镜像。
- 对Docker化程序和原生程序进行性能测试对比。
- 如果Docker出现不可控的风险,是否有替代方案。
- 是否需要对Docker容器做资源限制。
- 容器安全管理。
- 内部私有仓库的管理。
- 建议一个容器内只运行一个应用进程。
- Vagrant适合管理虚拟机,而Docker适合管理应用环境。Docker不是虚拟机,而是进程隔离,对于资源的消耗很少,但是目前需要Linux环境支持。Vagrant是虚拟机上做的封装,虚拟机本身会消耗资源。
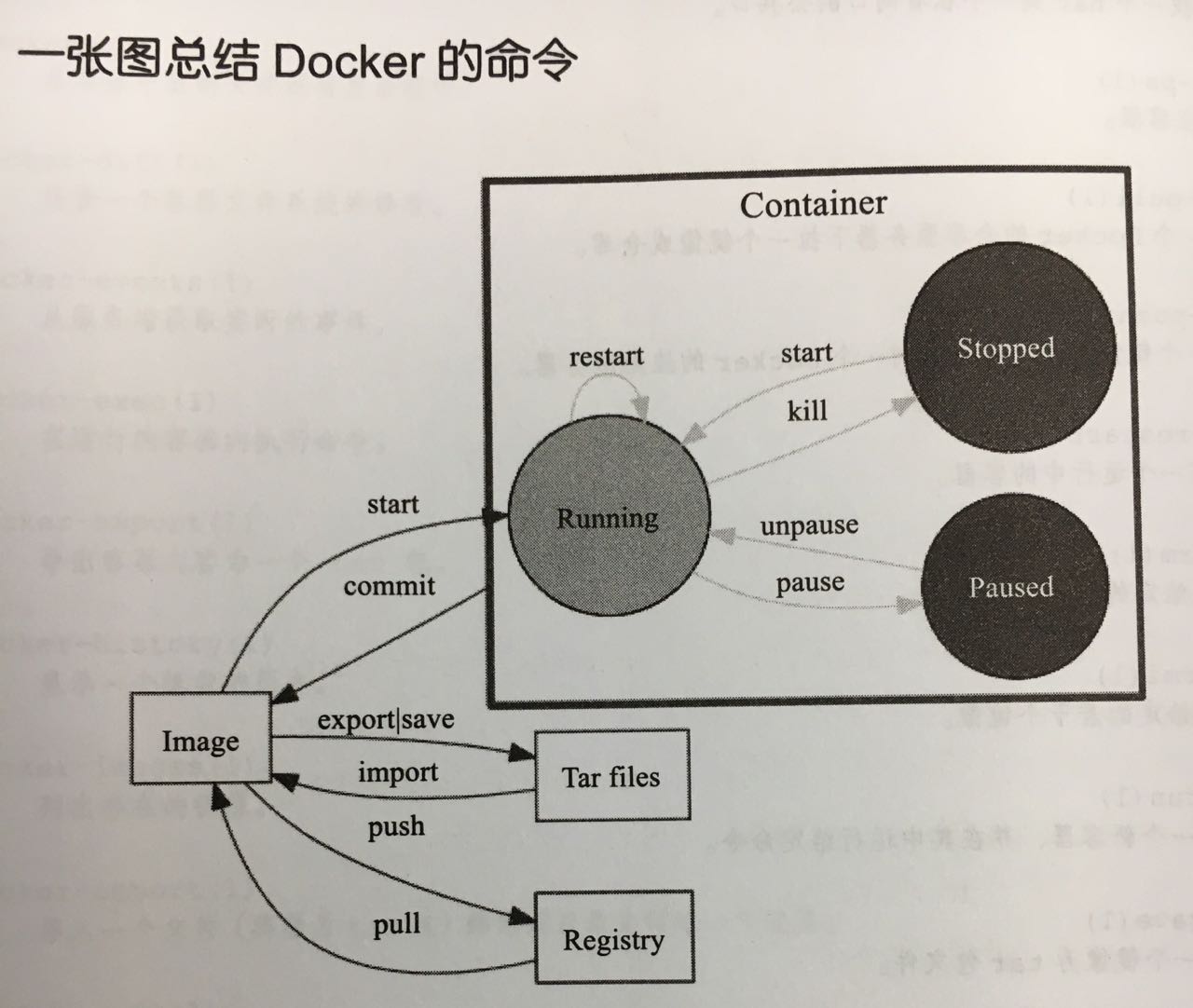
常用命令
docker build
https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/build/
docker build -t vieux/apache:2.0 .
容器指标
cAdvisor (Container Advisor) provides container users an understanding of the resource usage and performance characteristics of their running containers. It is a running daemon that collects, aggregates, processes, and exports information about running containers. Specifically, for each container it keeps resource isolation parameters, historical resource usage, histograms of complete historical resource usage and network statistics. This data is exported by container and machine-wide.
测试使用 (CentOS)
$docker version
Client:
Version: 18.09.7
API version: 1.39
Go version: go1.10.8
Git commit: 2d0083d
Built: Thu Jun 27 17:56:06 2019
OS/Arch: linux/amd64
Experimental: false
Server: Docker Engine - Community
Engine:
Version: 18.09.7
API version: 1.39 (minimum version 1.12)
Go version: go1.10.8
Git commit: 2d0083d
Built: Thu Jun 27 17:26:28 2019
OS/Arch: linux/amd64
Experimental: false
$docker info
Containers: 0
Running: 0
Paused: 0
Stopped: 0
Images: 9
Server Version: 18.09.7
Storage Driver: overlay2
Backing Filesystem: extfs
Supports d_type: true
Native Overlay Diff: false
Logging Driver: json-file
Cgroup Driver: cgroupfs
Plugins:
Volume: local
Network: bridge host macvlan null overlay
Log: awslogs fluentd gcplogs gelf journald json-file local logentries splunk syslog
Swarm: inactive
Runtimes: runc
Default Runtime: runc
Init Binary: docker-init
containerd version: 894b81a4b802e4eb2a91d1ce216b8817763c29fb
runc version: 425e105d5a03fabd737a126ad93d62a9eeede87f
init version: fec3683
Security Options:
seccomp
Profile: default
Kernel Version: 3.10.107-1-tlinux2_kvm_guest-0049
Operating System: Tencent tlinux 2.2 (Final)
OSType: linux
Architecture: x86_64
CPUs: 16
Total Memory: 31.17GiB
Name: VM-11-48-centos
ID: OLLW:ZRBS:Z2XV:34ER:NKGJ:NNH4:LKOX:YX3U:BSDO:SL2I:F7S7:CMSM
Docker Root Dir: /data/docker
Debug Mode (client): false
Debug Mode (server): false
Registry: https://index.docker.io/v1/
Labels:
Experimental: false
Insecure Registries:
bk.artifactory.oa.com:8080
csighub.tencentyun.com
docker.oa.com:8080
hub.oa.com
127.0.0.0/8
Registry Mirrors:
http://docker.oa.com:8080/
http://csighub.tencentyun.com/
Live Restore Enabled: false
Product License: Community Engine
用户管理
sudo service docker start # 启动 docker 服务
sudo usermod -aG docker ${USER} # 当前用户加入 docker 组
说明:
service docker start 是启动 Docker 的后台服务
usermod -aG 是把当前的用户加入 Docker 的用户组。这是因为操作 Docker 必须要有 root 权限,而直接使用 root 用户不够安全,加入 Docker 用户组是一个比较好的选择,这也是 Docker 官方推荐的做法。当然,如果只是为了图省事,也可以直接切换到 root 用户来操作 Docker
Dockerfile
- https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/builder/
CMD
The CMD instruction has three forms:
CMD ["executable","param1","param2"] (exec form, this is the preferred form)
CMD ["param1","param2"] (as default parameters to ENTRYPOINT)
CMD command param1 param2 (shell form)
There can only be one CMD instruction in a Dockerfile. If you list more than one CMD then only the last CMD will take effect.
The main purpose of a CMD is to provide defaults for an executing container. These defaults can include an executable, or they can omit the executable, in which case you must specify an ENTRYPOINT instruction as well.
If CMD is used to provide default arguments for the ENTRYPOINT instruction, both the CMD and ENTRYPOINT instructions should be specified with the JSON array format.
The exec form is parsed as a JSON array, which means that you must use double-quotes (“) around words not single-quotes (‘).
If you use the shell form of the CMD, then the <command> will execute in /bin/sh -c:
FROM ubuntu
CMD echo "This is a test." | wc -
If you want to run your <command> without a shell then you must express the command as a JSON array and give the full path to the executable. This array form is the preferred format of CMD. Any additional parameters must be individually expressed as strings in the array:
FROM ubuntu
CMD ["/usr/bin/wc","--help"]
If you would like your container to run the same executable every time, then you should consider using ENTRYPOINT in combination with CMD. See ENTRYPOINT.
If the user specifies arguments to
docker runthen they will override the default specified inCMD.
ENTRYPOINT
Q&A
How can I find a Docker image with a specific tag in Docker registry on the Docker command line?
I try to locate one specific tag for a Docker image. How can I do it on the command line? I want to avoid downloading all the images and then removing the unneeded ones.
Answers:
#!/usr/bin/bashs
# docker_remote_tags.sh
curl -s -S "https://registry.hub.docker.com/v2/repositories/library/$@/tags/" | jq '."results"[]["name"]' | sort
历史文章
书籍
优化
官方文档
- https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/run/
- Docker Release Notes
- Docker development best practices