TLS in Action
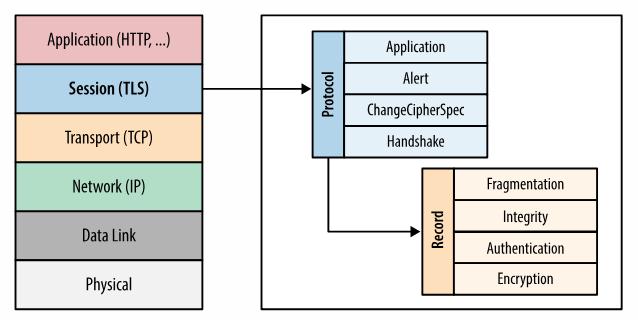
TLS协议原理
TLS(Transport Layer Security)协议的基本原理是,采用Public-key cryptography,客户端先向服务器端索要公钥,然后用公钥加密信息,服务器收到密文后,用自己的私钥解密,最后协商出一个会话密钥。
思考:
- 如何保证公钥不被篡改?解决方法:将公钥放在数字证书(Public-key cryptography)中。只要证书是可信的,公钥就是可信的。
- 公钥加密计算量太大,如何减少耗用的时间?解决方法:每一次会话,客户端和服务器端都生成一个会话密钥,用它来加密信息。由于会话密钥是对称加密,所以运算速度非常快,而服务器公钥只用于加密会话密钥本身,这样就减少了加密运算的消耗时间。
Note: When the SSL protocol was standardized by the IETF, it was renamed to Transport Layer Security (TLS). Many use the TLS and SSL names interchangeably, but technically, they are different, since each describes a different version of the protocol.
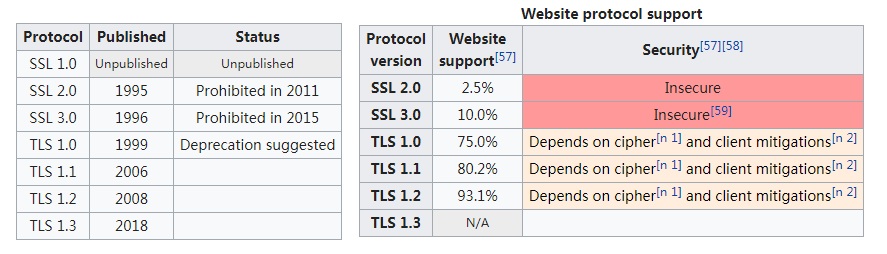
TLS协议的发展历史
- 1994年,NetScape公司设计了SSL协议(Secure Sockets Layer)的1.0版,但是未发布。
- 1995年,NetScape公司发布SSL 2.0版,很快发现有严重漏洞。
- 1996年,SSL 3.0版问世,得到大规模应用。
- 1999年,互联网标准化组织ISOC接替NetScape公司,发布了SSL的升级版TLS 1.0版。
- 2006年和2008年,TLS进行了两次升级,分别为TLS 1.1版和TLS 1.2版。
- 2018年8月,发布TLS 1.3版。
TLS协议的交互流程
- 客户端向服务器端索要并验证公钥。
- 双方协商生成会话密钥。
- 双方采用会话密钥进行加密通信。
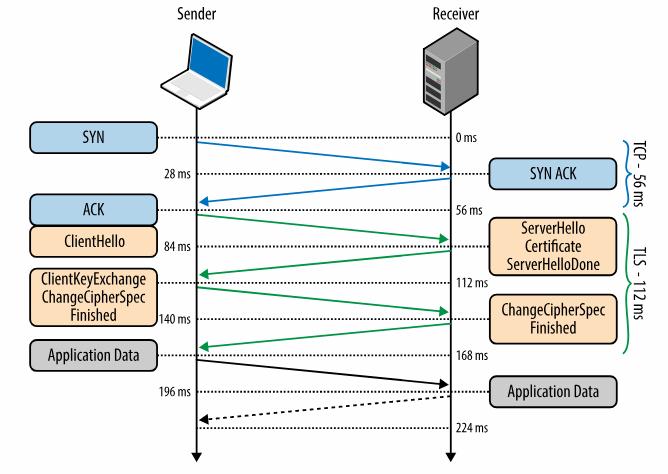
Note: Assumes the optimistic 28 millisecond one-way “light in fiber” delay between New York and London in TCP connection establishment.
TLS的性能问题
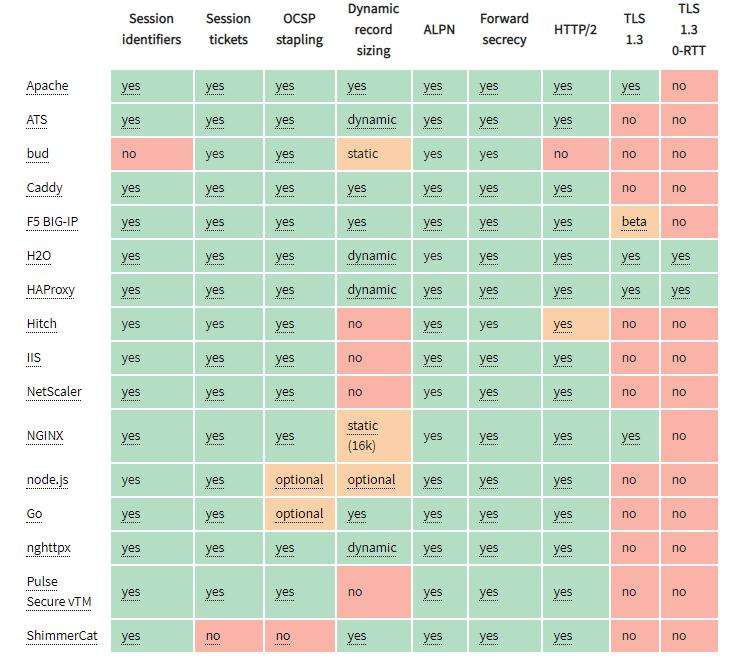
在TLS has exactly one performance problem文中,指出了一些针对TLS性能优化的方法。
- 使用专门的硬件,而非通用的CPU
- TLS resumption and TLS False Start
目前主流Server对性能优化特性的支持情况:
- resumption
- OCSP stapling
- false start (requires ALPN and forward secrecy)
- HTTP/2 protocol