CPP Algorithm
- 2021 TPC腾讯程序设计竞赛 Beautiful Sequence (正赛)
- 2020 TPC腾讯程序设计竞赛 Source of Happiness (正赛)
- 2020 TPC腾讯程序设计竞赛 Not Fibonacc (正赛)
- 2020 TPC腾讯程序设计竞赛 A IPv6 (正赛)
- 2020 TPC腾讯程序设计竞赛 Group the Integers (正赛)
- 2020 TPC腾讯程序设计竞赛 A Easy Task (热身赛)
- 单链表逆序
- LRU简单实现
- 封装迭代器
- 判断是否是闰年
- 随机数
2021 TPC腾讯程序设计竞赛 Beautiful Sequence (正赛)
一个序列 b1,b2, … ,bn 是美丽序列,当对所有 1 <= i < n 有 bi * bi+1 <= 0,给定一个整数序列 a1,a2, … ,an 问是否可以通过重新排列其中的元素使其变为美丽序列。
Input:
有多组测试数据,第一行输入一个整数 T 代表测试数据组数。对于每组测试数据: 第一行输入一个整数 n (2 <= n <= 10^5) 表示序列的长度 第二行输入 n 个整数 a1,a2, … , an (-10^9 <= ai <= 10^9)表示序列的元素 保证所以数据 n 之和不超过 10^6
Output:
每组数据输出一行。若可以通过重新排列使得序列变为美丽序列输出 Yes,否则输出 No
Sample Input:
3
3
0 1 -1
5
2 3 4 -2 -3
5
5 5 5 5 5
Sample Output:
Yes
Yes
No
解题思路:记x为序列中正数的数量,y为序列中负数的数量,z为序列中零的数量,判断max(x,y) - min(x,y) <= z + 1即可。
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--)
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
int x, y, z;
x = y = z = 0;
for (int i = 0; i != n; ++i)
{
int m;
scanf("%d", &m);
if (m == 0) ++z;
else if (m < 0) ++x;
else if (m > 0) ++y;
}
auto diff = 0;
if (x < y) diff = y - x;
else if (x > y) diff = x - y;
if (diff <= z + 1) printf("Yes\n");
else printf("No\n");
}
return 0;
}
package main
import (
"bufio"
"fmt"
"os"
"strconv"
"strings"
)
func ReadLine(reader *bufio.Reader) string {
line, _ := reader.ReadString('\n')
return strings.TrimRight(line, "\n")
}
func ReadInt(reader *bufio.Reader) int {
num, _ := strconv.Atoi(ReadLine(reader))
return num
}
func ReadArray(reader *bufio.Reader) []int {
line := ReadLine(reader)
strs := strings.Split(line, " ")
nums := make([]int, len(strs))
for i, s := range strs {
nums[i], _ = strconv.Atoi(s)
}
return nums
}
func main() {
reader := bufio.NewReader(os.Stdin)
T := ReadInt(reader)
for i := 0; i < T; i++ {
x := 0
y := 0
z := 0
diff := 0
ReadInt(reader)
m := ReadArray(reader)
for _, t := range m {
if t == 0 {
z++
} else if t > 0 {
x++
} else {
y++
}
}
if x > y {
diff = x - y
} else {
diff = y - x
}
if diff <= z+1 {
fmt.Println("Yes")
} else {
fmt.Println("No")
}
}
}
2020 TPC腾讯程序设计竞赛 Source of Happiness (正赛)
The famous instant message software QQ has recently released its badge system. Users are awarded with different types of badges when using the software if they meet certain conditions. One of the badge, the Source of Happiness badge, requires the users to send at least m memes in total during 3 continuous days. The user will be awarded with Source of Happiness at the end of the 3rd day.
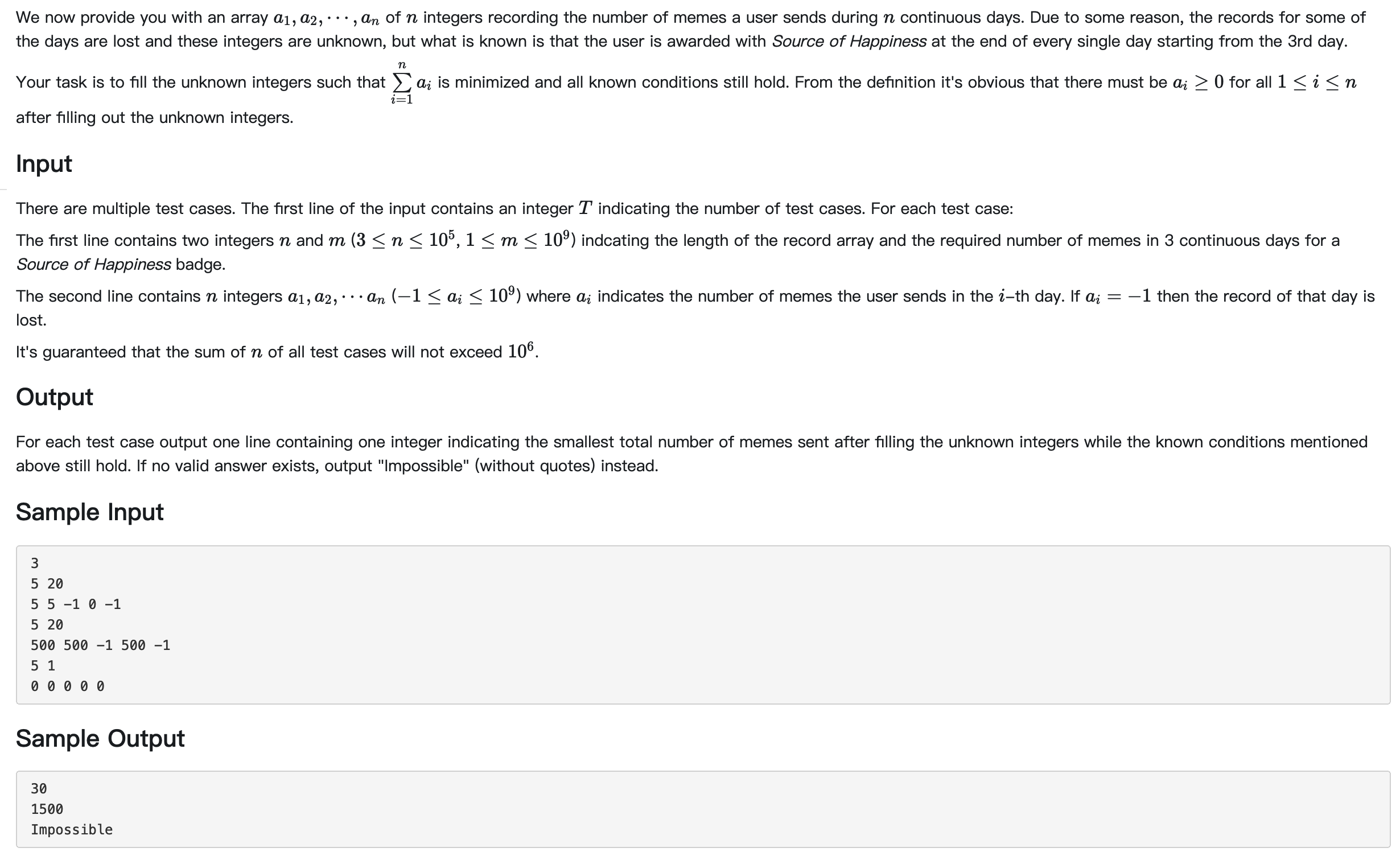
Hint:
For the first sample test case, one valid record array after filling the unknown integers is {5, 5, 15, 0, 5}, so the answer is 5 + 5 + 15 + 0 + 5 = 30.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <algorithm>
typedef struct A {
long long ori;
long long cur;
} t_a;
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--) {
int n, m;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
std::list<t_a> v;
long long res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
t_a a;
a.ori = a.cur = x;
v.emplace_back(a);
if (a.ori != -1) {
res += a.ori;
}
}
bool impos = false;
while (v.size() > 2) {
std::list<int> lost_pos_list;
long long has = 0;
auto iter = v.begin();
for (int i = 1; iter != v.end(); ++iter, ++i) {
if (iter->ori == -1) {
lost_pos_list.emplace_back(i - 1);
}
if (iter->cur != -1) {
has += iter->cur;
}
if (i % 3 == 0) {
if (has < m) {
if (lost_pos_list.empty()) {
impos = true;
break;
}
auto update_idx = lost_pos_list.back();
auto update_iter = v.begin();
for (int i = 0; i != update_idx; ++i, ++update_iter);
int left = m - has;
res += left;
update_iter->cur = std::max(update_iter->cur, 0LL) + left;
}
v.pop_front();
break;
}
}// for
if (impos) {
break;
}
}// while
if (impos) {
printf("Impossible\n");
} else {
printf("%lld\n", res);
}
}// while
return 0;
}
2020 TPC腾讯程序设计竞赛 Not Fibonacc (正赛)
二进制字符串是由数字 0 和 1 组成的字符串。给定一个二进制字符串 s=s1s2…sn(n >= 3),您需要将里面的数字重新排列,使得重新排列后的字符串对于所有 3 <= i <= n 满足 s(i-2) + s(i-1) != s(i)。 输入格式:
有多组测试数据。第一行输入一个整数 T 代表测试数据组数。对于每组测试数据:
第一行输入一个二进制字符串 s (3 <= num(s) <= 10^5, s(i) ∈ {0, 1}),保证所有数据中 num(s) 之和不超过 10^6。
输出格式:
对于每组数据,若存在符合要求的重排列,输出一行重排列后的字符串(若有多种合理答案,您可以输出任意一种),否则输出 “Impossible”(不输出引号)。
样例输入:
2
01110
000
样例输出:
11100
Impossible
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
std::string proc(const std::string &str)
{
int cnt1 = 0, cnt0 = 0;
for (auto &c : str) {
if (c == '0') {
++cnt0;
} else if (c == '1') {
++cnt1;
}
}
std::string ans;
while (cnt0 >= 2 && cnt1 >= 1) {
ans += "001";
cnt0 -= 2;
--cnt1;
}
if (cnt0 > 2 && cnt1 == 0) {
return "Impossible";
}
ans += std::string(cnt0, '0');
ans.insert(0, cnt1, '1');
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int n = 0;
std::cin >> n;
while (n-- > 0) {
std::string str;
std::cin >> str;
std::cout << proc(str) << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
2020 TPC腾讯程序设计竞赛 A IPv6 (正赛)
网际协议第 6 版(IPv6)是网际协议(IP)的最新版本。该协议用以鉴别并定位网络上的计算机,并对网络流量进行路由。该协议使用 128 个二进制位代表一个网络地址,其设计目的是为了替换第 4 版协议。
IPv6 的 128 位地址可以分为 8 组,每组各 16 位。我们可以将每组二进制位写成 4 个十六进制数,各组之间用冒号(:)分隔。例如,2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:ff00:0042:8329 就是一个 IPv6 地址。
方便起见,一个 IPv6 地址可以按以下规则缩写为一个更加简短的表现形式:
- 每一组十六进制数的前导零会被去除。例如,0042 将变为 42。
- 连续多组十六进制表示的 0 会被一对双冒号(::)替换。请注意,一个地址中双冒号至多出现一次,否则该缩写对应的完整 IPv6 地址可能无法确定。
以下是这些简写规则的使用范例:
- 完整 IPv6 地址:2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:ff00:0042:8329
- 去除每组十六进制数中的前导零后:2001:db8:0:0:0:ff00:42:8329
- 省略连续的十六进制零后:2001:db8::ff00:42:8329
根据上述规则,回环地址 0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0001 可以被简写为 ::1
你的任务就是将一个缩写后的 IPv6 地址改写为一个完整的地址。
输入格式:
有多组测试数据。第一行输入一个整数 T(约 1000)代表测试数据组数。对于每组测试数据:
第一行输入一个字符串 s 代表一个合法的缩写后的 IPv6 地址,保证 s 只包含数字、小写字母和冒号。
输出格式:
每组数据输出一行一个字符串,代表完整的 IPv6 地址。
样例输入:
4
7abc::00ff:fffc
fc:0:0:8976:0:0:0:ff
2c0f:9981::
::
样例输出:
7abc:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:00ff:fffc
00fc:0000:0000:8976:0000:0000:0000:00ff
2c0f:9981:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000
0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
bool g_find_double_colon = false;
std::vector<std::string> g_res_vec;
void split_str(const std::string& str, const std::string& delimiters, std::vector<std::string>& tokens)
{
// skip delimiters at beginning
// ,a,b,c, -> [a, b, c]
std::string::size_type lastPos = str.find_first_not_of(delimiters, 0);
std::string::size_type pos = str.find_first_of(delimiters, lastPos);
while (std::string::npos != pos || std::string::npos != lastPos)
{
tokens.push_back(str.substr(lastPos, pos - lastPos));
lastPos = str.find_first_not_of(delimiters, pos);
pos = str.find_first_of(delimiters, lastPos);
}
return;
}
void replace(std::string& str)
{
// :: -> :*:
size_t index = str.find("::");
if (index != std::string::npos) {
str.replace(index, 2, ":*:");
}
return;
}
void print_res(const std::string& s)
{
// print ab -> 00ab
size_t s_len = s.length();
if (s_len != 4) {
for (size_t i = 0; i != 4 - s_len; ++i) {
printf("0");
}
printf("%s", s.c_str());
} else {
printf("%s", s.c_str());
}
return;
}
void func()
{
// ex. 0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000
char s[64] = {0};
scanf("%s", s);
std::string src = s;
size_t src_len = src.length();
// :: has only one in IPv6
size_t found = src.find("::");
if (found != std::string::npos) {
// a::b:c -> a:*:b:c
replace(src);
std::vector<std::string> colon_vec;
split_str(src, ":", colon_vec);
size_t colon_vec_size = colon_vec.size();
size_t left_size = 8 - (colon_vec_size - 1);
for (auto& item : colon_vec) {
//printf("item[%s]\n", item.c_str());
if (item != "*") {
g_res_vec.push_back(item);
} else {
for (size_t i = 0; i != left_size; ++i) {
g_res_vec.push_back("0000");
}
}
}
} else {
// no find ::
std::vector<std::string> colon_vec;
split_str(src, ":", colon_vec);
for (auto& item : colon_vec) {
g_res_vec.push_back(item);
}
}
size_t i = 1;
for (auto& res : g_res_vec) {
if (i < g_res_vec.size()) {
print_res(res);
printf(":");
} else {
print_res(res);
printf("\n");
}
++i;
}
return;
}
int main()
{
int group_cnt = 0;
scanf("%d", &group_cnt);
for (int i = 0; i != group_cnt; ++i) {
g_res_vec.clear();
func();
}
return 0;
}
2020 TPC腾讯程序设计竞赛 Group the Integers (正赛)
请将从 1 至 n (包括 1 与 n)的所有整数分成若干组,使得每一组内的整数互质。每个整数应恰好属于一个分组。求最少的分组数。
输入格式:
有多组测试数据。第一行输入一个整数 T(约 10^5)代表测试数据组数。对于每组测试数据:第一行输入一个整数 n(1 ≤ n ≤ 10^9)。
输出格式:
每组数据输出一行一个整数,代表最少分组数。
样例输入:
2
2
5
样例输出:
1
2
样例说明:
对于第二组样例数据,我们可以将整数划分为 {1, 2, 3, 5} 和 {4} 两组。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
void func()
{
int last = 0;
scanf("%d", &last);
if (last == 1) printf("%d\n", last);
else printf("%d\n", last / 2);
return;
}
int main()
{
int group_cnt = 0;
scanf("%d", &group_cnt);
for (int i = 0; i != group_cnt; ++i) {
func();
}
return 0;
}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
int main()
{
int T, n;
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T--) {
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("%d\n", std::max(1, n >> 1));
}
return 0;
}
使用GoLang实现:
package main
import (
"bufio"
"fmt"
"os"
"strconv"
"strings"
)
func ReadLine(reader *bufio.Reader) string {
line, _ := reader.ReadString('\n')
return strings.TrimRight(line, "\n")
}
func ReadInt(reader *bufio.Reader) int {
num, _ := strconv.Atoi(ReadLine(reader))
return num
}
func ReadArray(reader *bufio.Reader) []int {
line := ReadLine(reader);
strs := strings.Split(line, " ")
nums := make([]int, len(strs))
for i, s := range strs {
nums[i], _ = strconv.Atoi(s)
}
return nums
}
func main() {
reader := bufio.NewReader(os.Stdin)
T := ReadInt(reader)
for casi := int(0); casi < T; casi++ {
n := ReadInt(reader)
n = n / 2
if n == 0 {
n = 1
}
fmt.Println(n)
}
}
2020 TPC腾讯程序设计竞赛 A Easy Task (热身赛)
给定 n 个整数,每次可以进行如下操作:选择其中最大的整数 a 与最小的整数 b,并将它们都替换为 (a−b)。是否可以在有限次操作内使得所有整数都相等?如果是,最后的结果是什么?
输入格式:
有多组测试数据。第一行输入一个整数 T(约 20)代表测试数据组数。对于每组测试数据: 第一行输入一个整数 n(2≤n≤10)代表给定整数的数量。 第二行输入 n 个整数 a1, a2, …, an (-10 ^ 5 <= ai <= 10 ^ 5) 代表给定的整数。
输出格式:
每组数据输出一行。若可以将所有整数变为相等,输出最终产生的那个整数;否则输出 “Impossible”(不输出引号)。
样例输入:
2
3
1 2 3
2
5 5
样例输出:
2
5
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
int main()
{
int cas;
scanf("%d", &cas);
while (cas--) {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
std::multiset<int> a;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
a.insert(x);
}
while (*a.begin() != *a.rbegin()) {
auto p1 = a.begin();
auto p2 = std::prev(a.end());
a.erase(p1);
a.erase(p2);
int nval = *p2 - *p1;
a.insert(nval);
a.insert(nval);
}
printf("%d\n", *a.begin());
}
return 0;
}
单链表逆序
已知链表的头结点head, 写一个函数把这个链表逆序(即1->2->3转变为3->2->1)
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#define E_OK 0
#define E_FAIL 1
struct _Node
{
_Node(int i) { data = i; }
int data;
_Node *next;
};
typedef struct _Node Node;
Node* createList(int len)
{
Node* head = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i != len; ++i) {
Node* node = new Node(len - i);
node->next = head;
head = node;
}
return head;
}
void prinNode(Node* head)
{
Node* cur = head;
while (cur != NULL) {
printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void reverseList(Node** head)
{
Node* last = *head;
Node* cur = (*head)->next;
Node* pre = NULL;
while (cur != NULL) {
pre = cur->next;
cur->next = last;
last = cur;
cur = pre;
}
(*head)->next = NULL;
*head = last;
}
void deleteList(Node* head)
{
Node* cur;
while (head != NULL) {
cur = head;
head = head->next;
delete cur;
}
}
void test(int cnt)
{
Node* head = createList(cnt);
prinNode(head);
reverseList(&head);
prinNode(head);
deleteList(head);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
test(3);
test(5);
printf("done\n");
return E_OK;
}
LRU简单实现
设计和实现一种LRU cache(Least Recently Used cache), 支持get和set操作。
get(key): 如果key存在key中则返回对应的value, 否则返回 -1set(key, value): 更新key对应的value, 如果key不存在则插入对应的key, value。如果cache达到容量则淘汰最久未使用的键值对之后再插入
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <unordered_map>
#define E_OK 0
#define E_FAIL 1
#define E_NOT_FOUND -1
class LRUCache
{
public:
typedef typename std::pair<int, int> kv_t;
typedef typename std::list<kv_t>::iterator list_iterator_t;
LRUCache(int capacity)
{
m_max_size = capacity;
}
int get(int key)
{
auto it = m_cache_map.find(key);
if (it == m_cache_map.end()) {
return E_NOT_FOUND;
} else {
// move get item to begin position
m_cache_list.splice(m_cache_list.begin(), m_cache_list, it->second);
return it->second->second;
}
}
void set(int key, int value)
{
m_cache_list.push_front(kv_t(key, value));
// find it from cache
auto it = m_cache_map.find(key);
if (it != m_cache_map.end()) {
// delete origin item
m_cache_list.erase(it->second);
m_cache_map.erase(it);
}
m_cache_map[key] = m_cache_list.begin();
// check size and delete last one
if (m_cache_map.size() > m_max_size) {
auto last = m_cache_list.end();
last--;
m_cache_map.erase(last->first);
m_cache_list.pop_back();
}
}
private:
std::list<kv_t> m_cache_list;
std::unordered_map<int, list_iterator_t> m_cache_map;
int m_max_size;
};
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
LRUCache lru(2);
lru.set(1, 1);
printf("lru.get(1) = %d\n", lru.get(1));
printf("lru.get(2) = %d\n", lru.get(2));
lru.set(2, 2);
printf("lru.get(2) = %d\n", lru.get(2));
lru.set(3, 3);
printf("lru.get(1) = %d\n", lru.get(1));
printf("done\n");
return E_OK;
}
/*
g++ -std=c++11 -o lru_cache lru_cache.cpp
lru.get(1) = 1
lru.get(2) = -1
lru.get(2) = 2
lru.get(1) = -1
done
*/
refer: https://github.com/lamerman/cpp-lru-cache/blob/master/include/lrucache.hpp
封装迭代器
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <iterator>
using record = std::map<std::string, std::string>;
class A
{
public:
record m_var{
{"a", "b"},
{"c", "d"}
};
};
class B
{
public:
class iterator {
public:
using value_type = std::string;
using reference = const value_type&;
using pointer = const value_type*;
iterator(const std::string tag, record *ref) : m_ref(ref), m_iter(ref->end()) {}
iterator(record *ref) : m_ref(ref), m_iter(ref->begin()) {
}
reference operator*() const noexcept {
return m_iter->first;
}
iterator& operator++() {
++m_iter;
return *this;
}
bool operator==(const iterator& rhs) const noexcept {
return m_iter == rhs.m_iter;
}
bool operator!=(const iterator& rhs) const noexcept {
return !operator==(rhs);
}
private:
record* m_ref;
record::iterator m_iter;
};
B(record* ref) : m_ref(ref) {
}
iterator begin() {
return iterator(m_ref);
}
iterator end() const noexcept {
return iterator("END", m_ref);
}
private:
record* m_ref;
};
int main()
{
A a;
for (auto& v : a.m_var) {
std::cout << v.first << "\n";
}
B b(&a.m_var);
for (auto& v : b) {
std::cout << v << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
refer:
- http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/iterator/
- https://zh.cppreference.com/w/cpp/iterator/iterator_tags
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/8054273/how-to-implement-an-stl-style-iterator-and-avoid-common-pitfalls/8054856
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/7758580/writing-your-own-stl-container/7759622#7759622
- https://www.fluentcpp.com/2018/05/08/std-iterator-deprecated/
判断是否是闰年
判断闰年时有两个条件:
-
year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0:这一条件用于判断非整百年份。能被4整除的年份通常是闰年,但整百年份是个例外。所以需要排除能被100整除的情况,确保只有非整百年份且能被4整除的才是闰年。例如,2024年能被4整除且不能被100整除,是闰年;而1900年能被4整除,但也能被100整除,不符合该条件,不是闰年。 -
year % 400 == 0:这是针对整百年份的判断条件。整百年份必须能被400整除才是闰年。例如,2000年能被400整除,是闰年;1900年不能被400整除,不是闰年。
通过这两个条件的组合使用,就可以准确判断任意一个年份是否为闰年。
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int year;
printf("请输入一个年份: ");
scanf("%d", &year);
if ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)) {
printf("%d年是闰年。\n", year);
} else {
printf("%d年不是闰年。\n", year);
}
return 0;
}
随机数
伪随机数生成器
rand, rand_r, srand — pseudo-random number generator (伪随机数生成器)
参考:
- https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man3/rand.3p.html
- https://linux.die.net/man/3/rand_r
- https://linux.die.net/man/3/drand48_r
- https://linux.die.net/man/3/random
#include <stdlib.h>
int rand(void);
int rand_r(unsigned int *seedp);
void srand(unsigned int seed);
The rand() function returns a pseudo-random integer in the range 0 to RAND_MAX inclusive (i.e., the mathematical range [0, RAND_MAX]).
The srand() function sets its argument as the seed for a new sequence of pseudo-random integers to be returned by rand(). These sequences are repeatable by calling srand() with the same seed value.
If no seed value is provided, the rand() function is automatically seeded with a value of 1.
The function rand() is not reentrant or thread-safe, since it uses hidden state that is modified on each call. This might just be the seed value to be used by the next call, or it might be something more elaborate. In order to get reproducible behavior in a threaded application, this state must be made explicit; this can be done using the reentrant function rand_r().
Like rand(), rand_r() returns a pseudo-random integer in the range [0, RAND_MAX]. The seedp argument is a pointer to an unsigned int that is used to store state between calls. If rand_r() is called with the same initial value for the integer pointed to by seedp, and that value is not modified between calls, then the same pseudo-random sequence will result.
The value pointed to by the seedp argument of rand_r() provides only a very small amount of state, so this function will be a weak pseudo-random generator. Try drand48_r(3) instead.
Note: drand48_r(3), These functions are GNU extensions and are not portable.
Return Value
The rand() and rand_r() functions return a value between 0 and RAND_MAX (inclusive). The srand() function returns no value.
Generating the Same Sequence on Different Machines
POSIX.1-2001 gives the following example of an implementation of rand() and srand(), possibly useful when one needs the same sequence on two different machines.
static unsigned long next = 1;
/* RAND_MAX assumed to be 32767 */
int myrand(void) {
next = next * 1103515245 + 12345;
return((unsigned)(next/65536) % 32768);
}
void mysrand(unsigned seed) {
next = seed;
}
Generating a Pseudo-Random Number Sequence
The following program can be used to display the pseudo-random sequence produced by rand() when given a particular seed.
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int j, r, nloops;
unsigned int seed;
if (argc != 3) {
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s <seed> <nloops>\n", argv[0]);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
seed = atoi(argv[1]);
nloops = atoi(argv[2]);
srand(seed);
for (j = 0; j < nloops; j++) {
r = rand();
printf("%d\n", r);
}
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
基于权重的随机选择算法
权重随机选择:在多个选项中,根据每个选项的权重(概率)进行随机选择,权重越大的选项被选中的概率越高。
refer:
- 加权随机采样 (Weighted Random Sampling) 文章中介绍了 A-Res 与 A-ExpJ 两种算法,按照步骤用 Python 实现了一个简单的版本,最后用采样的方式验证了算法的正确性。
- Weighted Random Sampling (2005; Efraimidis, Spirakis) (paper)
- Weighted random sampling with a reservoir (2006) (paper)
累积概率分布
将各个选项的概率依次累加,形成一个递增的序列,用于快速定位随机数对应的选项。
算法描述:
- 如果权重为0,直接返回成功(权重为0的元素不会被选中)
- 计算新元素的累积概率 = 前一个元素的累积概率 + 当前元素权重
- 检查累积概率是否超出安全范围(避免溢出和超出随机数范围)
- 创建新的随机信息结构并添加到候选池中
基于权重,随机选择一个(不删除)
算法描述:
- 构建累积概率分布
假设有4个元素,权重分别为:[10, 20, 30, 40]
元素索引: 0 1 2 3
权重概率: 10 20 30 40
累积概率: 10 30 60 100
struct STRandInfo
{
uint32_t m_uProb; // 当前元素的权重概率
uint32_t m_uAccProb; // 累积概率(当前元素及之前所有元素的权重之和)
UserDataType m_stUserData; // 用户数据
};
- 生成随机数
生成一个 [0, 总权重) 范围内的随机数,即 [0, 100)
- 二分查找定位
使用累积概率进行快速定位:
uint32_t uProb = rand() % uMaxProb; // 假设生成随机数 45
// 遍历查找第一个累积概率大于随机数的元素
for (size_t i = 0; i < m_stRandInfoVec.size(); ++i)
{
const STRandInfo& stRandInfo = m_stRandInfoVec[i];
if (stRandInfo.m_uAccProb > uProb) // 60 > 45,选中元素2
{
return &stRandInfo.m_stUserData;
}
}
使用示例:
// 游戏物品掉落系统示例
CRandomAgent<ItemData> dropTable;
// 添加物品及其掉落权重
dropTable.Add(10, ItemData{"普通剑", 100}); // 10% 概率
dropTable.Add(20, ItemData{"精良剑", 200}); // 20% 概率
dropTable.Add(30, ItemData{"稀有剑", 500}); // 30% 概率
dropTable.Add(40, ItemData{"传说剑", 1000}); // 40% 概率
// 随机选择掉落物品
const ItemData* droppedItem = dropTable.Rand();
- 概率准确性
- 完全按照权重比例进行选择
- 权重为 10 的元素被选中概率 = 10/100 = 10%
- 权重为 40 的元素被选中概率 = 40/100 = 40%
添加顺序不影响概率分布的原因:
无论元素以什么顺序添加到 m_stRandInfoVec 中,最终的累积概率分布都是相同的。算法只关心累积概率值,而不关心元素在数组中的位置。
- 累积概率的计算:每次添加新元素时,都会基于当前的总累积概率进行计算
- 数学原理:加法满足交换律,无论顺序如何,总权重不变
- 算法设计:Rand() 方法只依赖累积概率值,不依赖元素位置
- 最终结果:无论以什么顺序构建,最终的权重分布都是相同的
// 测试1:递增顺序
CRandomAgent<ItemData> table1;
table1.Add(10, ItemData{"A"});
table1.Add(20, ItemData{"B"});
table1.Add(30, ItemData{"C"});
table1.Add(40, ItemData{"D"});
// 测试2:递减顺序
CRandomAgent<ItemData> table2;
table2.Add(40, ItemData{"D"});
table2.Add(30, ItemData{"C"});
table2.Add(20, ItemData{"B"});
table2.Add(10, ItemData{"A"});
// 两个表的累积概率分布完全相同:
// 元素A: 10/100 = 10%
// 元素B: 20/100 = 20%
// 元素C: 30/100 = 30%
// 元素D: 40/100 = 40%
基于权重,随机选择一个(删除,不放回)
算法描述:
该方法从权重池中随机选择一个元素,选择后会将选中的元素从候选池中移除,确保不会重复选择同一个元素。适用于需要抽取单个物品且不重复的场景。
- 检查是否有可用的随机数据
- 生成一个
[0, 总权重)范围内的随机数 - 遍历所有元素,找到第一个累积概率大于随机数的元素
- 选中后从候选池中移除该元素,并调整后续元素的累积概率
- 返回选中的用户数据
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 为候选元素数量
- 空间复杂度:O(1),仅使用常数额外空间
基于权重,随机选择多个(不重复)
算法描述:
- 生成随机数:uProb = rand() % uMaxProb
- 线性扫描:从第一个元素开始,依次检查每个元素的权重
- 权重比较:如果 元素权重 > 随机数,则选中该元素
- 动态调整:
- 选中:从总权重中减去该元素权重
- 未选中:从随机数中减去该元素权重
概率分布正确性:
- 每次选择时,随机数的范围都是基于当前剩余元素的总权重
- 每个元素被选中的概率 = 该元素权重 / 当前总权重
- 选中后立即从候选池中移除,确保不重复
权重调整的正确性:
- uMaxProb -= stRandInfo.m_uProb:确保下次选择时总权重正确
- uProb -= stRandInfo.m_uProb:确保线性扫描时权重累加正确
示例说明:
假设有元素:[A(10), B(20), C(30), D(40)],总权重 100
第一次选择:
- 生成随机数:uProb = 45
- 检查 A:10 > 45?否,uProb = 45 - 10 = 35
- 检查 B:20 > 35?否,uProb = 35 - 20 = 15
- 检查 C:30 > 15?是,选中 C
- 调整总权重:uMaxProb = 100 - 30 = 70
第二次选择:
- 生成随机数:uProb = rand() % 70(假设生成 25)
- 检查 A:10 > 25?否,uProb = 25 - 10 = 15
- 检查 B:20 > 15?是,选中 B
- 调整总权重:uMaxProb = 70 - 20 = 50
算法实现
template < typename UserDataType>
class CRandomAgent
{
protected:
struct STRandInfo
{
uint32_t m_uProb;
uint32_t m_uAccProb;
UserDataType m_stUserData;
};
using RandInfoVec = std::vector<STRandInfo> ;
public:
void Reset()
{
m_stRandInfoVec.clear();
}
[[nodiscard]] uint32_t GetNum() const
{
return static_cast<uint32_t> (m_stRandInfoVec.size());
}
[[nodiscard]] uint32_t GetProbByIdx(uint32_t uIdx) const
{
if (uIdx >= m_stRandInfoVec.size())
{
ASSERT(0);
return 0;
}
return m_stRandInfoVec[uIdx].m_uProb;
}
const UserDataType &GetDataByIdx(uint32_t uIdx) const
{
return m_stRandInfoVec[uIdx].m_stUserData;
}
/**
*@brief 向权重随机选择器中添加新的候选元素
*
* 该方法用于向权重池中添加新的候选元素,每个元素都有一个权重概率。
* 系统会维护累积概率分布,用于后续的权重随机选择操作。
*
* 算法原理:
*1. 如果权重为0,直接返回成功(权重为0的元素不会被选中)
*2. 计算新元素的累积概率 = 前一个元素的累积概率 + 当前元素权重
*3. 检查累积概率是否超出安全范围(避免溢出和超出随机数范围)
*4. 创建新的随机信息结构并添加到候选池中
*
*时间复杂度:O(1),仅涉及向量末尾插入操作
*空间复杂度:O(1),仅创建单个 STRandInfo 结构
*
*@param uProb 元素的权重概率,必须大于0才有效
*@param stUserData 与权重关联的用户数据
*@return bool 成功返回 true,失败返回 false(如权重溢出或超出范围)
*/
bool Add(uint32_t uProb, const UserDataType &stUserData)
{
// 权重为0的元素不会被选中,直接返回成功
if (0 == uProb)
{
return true;
}
// 初始化累积概率
uint32_t uAccProb = 0;
// 如果候选池不为空,获取前一个元素的累积概率作为基础
if (m_stRandInfoVec.size() > 0)
{
uAccProb = m_stRandInfoVec.back().m_uAccProb;
}
// 安全地累加权重,避免整数溢出
SAFE_ADD(uAccProb, uProb);
// 检查累积概率是否超出安全范围
if (uAccProb == UINT32_MAX || uAccProb > static_cast<uint32_t> (RAND_MAX))
{
return false;
}
// 创建新的随机信息结构
STRandInfo stRandInfo;
stRandInfo.m_uProb = uProb; // 设置元素权重
stRandInfo.m_uAccProb = uAccProb; // 设置累积概率
stRandInfo.m_stUserData = stUserData; // 设置用户数据
// 将新元素添加到候选池末尾
m_stRandInfoVec.push_back(stRandInfo);
return true;
}
[[nodiscard]] bool Check() const
{
return static_cast<bool> (0 != m_stRandInfoVec.size());
}
/**
*@brief 进行单次不重复的权重随机选择 (不放回)
*
* 该方法从权重池中随机选择一个元素,选择后会将选中的元素从候选池中移除,
* 确保不会重复选择同一个元素。适用于需要抽取单个物品且不重复的场景。
*
* 算法原理:
*1. 检查是否有可用的随机数据
*2. 生成一个[0, 总权重) 范围内的随机数
*3. 遍历所有元素,找到第一个累积概率大于随机数的元素
*4. 选中后从候选池中移除该元素,并调整后续元素的累积概率
*5. 返回选中的用户数据
*
*时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 为候选元素数量
*空间复杂度:O(1),仅使用常数额外空间
*
*@param stData 输出参数,存储选中的用户数据
*@return bool 成功返回 true,失败返回 false(如候选池为空)
*/
bool RandWithoutReplacement(UserDataType & stData)
{
// 检查候选池是否为空
if (0 == m_stRandInfoVec.size())
{
return false;
}
// 获取总权重(最后一个元素的累积概率)
uint32_t uMaxProb = m_stRandInfoVec.back().m_uAccProb;
// 生成[0, uMaxProb) 范围内的随机数
uint32_t uProb = rand() % uMaxProb;
// 标记是否已选中元素
bool bIsSelect = false;
// 记录选中元素的迭代器位置
auto itorSelectitor = m_stRandInfoVec.end();
// 遍历所有候选元素,进行权重随机选择
for (auto iter = m_stRandInfoVec.begin(); iter != m_stRandInfoVec.end(); iter++)
{
STRandInfo &stRandInfo = *iter;
if (bIsSelect == true)
{
// 已选中元素后,需要调整后续元素的累积概率
// 减去已选中元素的权重,保持累积概率的正确性
stRandInfo.m_uAccProb -= itorSelectitor->m_uProb;
}
else if (stRandInfo.m_uAccProb > uProb)
{
// 找到第一个累积概率大于随机数的元素,选中该元素
bIsSelect = true;
// 记录选中元素的位置
itorSelectitor = iter;
// 保存选中的用户数据
stData = stRandInfo.m_stUserData;
}
}
// 检查是否成功选中元素
if (bIsSelect == false)
{
return false;
}
// 从候选池中移除已选中的元素
m_stRandInfoVec.erase(itorSelectitor);
return true;
}
/**
*@brief 根据权重进行随机选择,返回选中的用户数据指针
*
* 该方法使用累积概率分布进行权重随机选择。每个元素都有一个权重概率,
* 系统会根据权重随机选择一个元素并返回其用户数据。
*
* 算法原理:
*1. 计算总权重(最后一个元素的累积概率)
*2. 生成一个[0, 总权重) 范围内的随机数
*3. 遍历所有元素,找到第一个累积概率大于随机数的元素
*4. 返回该元素的用户数据指针
*
*@return const UserDataType* 返回选中的用户数据指针,如果没有数据或选择失败则返回 nullptr
*/
const UserDataType* Rand() const
{
// 检查是否有可用的随机数据
if (0 == m_stRandInfoVec.size())
{
return nullptr;
}
// 获取总权重(最后一个元素的累积概率)
uint32_t uMaxProb = m_stRandInfoVec.back().m_uAccProb;
// 生成[0, uMaxProb) 范围内的随机数
uint32_t uProb = rand() % uMaxProb;
// 遍历所有元素,根据累积概率进行权重随机选择
for (size_t i = 0; i < m_stRandInfoVec.size(); ++i)
{
const STRandInfo &stRandInfo = m_stRandInfoVec[i];
// 如果当前元素的累积概率大于随机数,则选中该元素
if (stRandInfo.m_uAccProb > uProb)
{
return &stRandInfo.m_stUserData;
}
}
// 理论上不应该到达这里,但为了安全起见返回 nullptr
return nullptr;
}
/**
*@brief 进行多次不重复的权重随机选择,返回选中的用户数据指针列表
*
* 该方法从权重池中随机选择指定数量的元素,每次选择后会将选中的元素从候选池中移除,
* 确保不会重复选择同一个元素。适用于需要抽取多个不同物品的场景。
*
* 算法原理:
*1. 创建候选索引列表,包含所有可用元素的索引
*2. 循环进行指定次数的随机选择:
* - 生成随机数
* - 遍历候选列表,根据权重进行选择
* - 选中后从候选列表移除,并调整总权重
*3. 返回所有选中元素的指针列表
*
*@param uRandNum 需要随机选择的数量
*@param stList 输出参数,存储选中元素的指针列表
*@return bool 成功返回 true,失败返回 false
*/
bool Rand(uint32_t uRandNum, PooledSTL::list<const UserDataType*> &stList) const
{
// 清空输出列表
stList.clear();
// 如果不需要选择任何元素,直接返回成功
if (0 == uRandNum)
{
return true;
}
// 检查是否有足够的元素可供选择
if (m_stRandInfoVec.size() < uRandNum)
{
return false;
}
// 获取初始总权重
uint32_t uMaxProb = m_stRandInfoVec.back().m_uAccProb;
// 创建候选索引列表,包含所有可用元素的索引
PooledSTL::list<uint32_t> stIdxList;
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < m_stRandInfoVec.size(); ++i)
{
stIdxList.push_back(i);
}
// 循环进行指定次数的随机选择
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < uRandNum; ++i)
{
// 生成[0, 当前总权重) 范围内的随机数
uint32_t uProb = rand() % uMaxProb;
// 遍历候选列表,根据权重进行选择
for (auto iter = stIdxList.begin(); iter != stIdxList.end(); ++iter)
{
const STRandInfo &stRandInfo = m_stRandInfoVec[*iter];
// 如果当前元素的权重大于随机数,则选中该元素
if (stRandInfo.m_uProb > uProb)
{
// 将选中的元素添加到结果列表
stList.push_back(&stRandInfo.m_stUserData);
// 从总权重中减去已选中元素的权重
uMaxProb -= stRandInfo.m_uProb;
// 从候选列表中移除已选中的元素
stIdxList.erase(iter);
break;
}
// 如果未选中,从随机数中减去当前元素的权重,继续检查下一个元素
uProb -= stRandInfo.m_uProb;
}
}
return true;
}
/**
*@brief 进行多次不重复的权重随机选择,返回选中的用户数据指针向量
*
*该方法是 Rand(uint32_t, PooledSTL::list <const UserDataType*>&) 的向量版本,
*功能完全相同,只是返回结果存储在 vector 容器中而不是 list 容器中。
*
* 实现方式:
*1. 调用 list 版本的 Rand 方法进行实际的随机选择
*2. 将结果从 list 容器复制到 vector 容器中
*3. 返回操作是否成功
*
*@param uRandNum 需要随机选择的数量
*@param stVector 输出参数,存储选中元素的指针向量
*@return bool 成功返回 true,失败返回 false
*/
bool Rand(uint32_t uRandNum, PooledSTL::vector<const UserDataType*> &stVector) const
{
// 清空输出向量
stVector.clear();
// 创建临时列表用于存储随机选择结果
PooledSTL::list<const UserDataType*> stList;
// 调用 list 版本的 Rand 方法进行实际的随机选择
if (Rand(uRandNum, stList))
{
// 将结果从 list 容器转存到 vector 容器
for (auto iter = stList.begin(); iter != stList.end(); ++iter)
{
stVector.push_back(*iter);
}
return true;
}
// 如果随机选择失败,返回 false
return false;
}
protected:
RandInfoVec m_stRandInfoVec;
};