Protolint in Action
- 基本用法
- Installation
- Usage
- Version Control Integration
- Editor Integration
- Call from Go code
- Rules
- Examples
- ENUM_FIELD_NAMES_PREFIX
- ENUM_FIELD_NAMES_UPPER_SNAKE_CASE
- ENUM_FIELD_NAMES_ZERO_VALUE_END_WITH
- ENUM_NAMES_UPPER_CAMEL_CASE
- FIELD_NAMES_LOWER_SNAKE_CASE
- IMPORTS_SORTED
- MESSAGE_NAMES_UPPER_CAMEL_CASE
- ORDER
- PACKAGE_NAME_LOWER_CASE
- RPC_NAMES_UPPER_CAMEL_CASE
- RPC_SERVICES_UPPER_CAMEL_CASE
- REPEATED_FIELD_NAMES_PLURALIZED
- INDENT
- QUOTE_CONSISTENT
- Creating your custom rules
- Reporters
- Configure
- Exit codes
- Refer
protolint is the pluggable linting/fixing utility for Protocol Buffer files (proto2+proto3):
- Runs fast because this works without compiler.
- Easy to follow the official style guide. The rules and the style guide correspond to each other exactly.
- Fixer automatically fixes all the possible official style guide violations.
- Allows to disable rules with a comment in a Protocol Buffer file.
- It is useful for projects which must keep API compatibility while enforce the style guide as much as possible.
- Some rules can be automatically disabled by inserting comments to the spotted violations.
- Loads plugins to contain your custom lint rules.
- Undergone testing for all rules.
- Many integration supports.
- protoc plugin
- Editor integration
- GitHub Action
- CI Integration
基本用法
查看所有规则
protolint list
常见规则:
根据 protolint list 的输出,常用规则包括:
MAX_LINE_LENGTH: 行长度限制(默认 80)IMPORTS_SORTED: 导入排序INDENT: 缩进风格SERVICE_NAMES_UPPER_CAMEL_CASE: 服务名大驼峰RPC_NAMES_UPPER_CAMEL_CASE: RPC 方法名大驼峰MESSAGE_NAMES_UPPER_CAMEL_CASE: 消息名大驼峰FIELD_NAMES_LOWER_SNAKE_CASE: 字段名小蛇形ENUM_FIELD_NAMES_UPPER_SNAKE_CASE: 枚举值名大蛇形REPEATED_FIELD_NAMES_PLURALIZED: repeated 字段使用复数
配置规则
方法 1: 使用内联注释禁用规则(推荐)
在 .proto 文件中使用注释来禁用特定规则:
// 在文件开头禁用 MAX_LINE_LENGTH 规则(项目规范是 120 字符)
// protolint:disable MAX_LINE_LENGTH
syntax = "proto3";
package jmesh.protocol;
// 对于特定行,可以使用 :next 或 :this
message VeryLongMessageNameThatExceedsTheDefaultLineLengthLimit {
// protolint:disable:next REPEATED_FIELD_NAMES_PLURALIZED
repeated string info = 1; // 这一行不会触发错误(:next 作用于下一行)
repeated string data = 2; // protolint:disable:this REPEATED_FIELD_NAMES_PLURALIZED 这一行不会触发错误(:this 作用于当前行)
}
// 重新启用规则
// protolint:enable MAX_LINE_LENGTH
方法 2: 使用自动修复和禁用注释
# 自动修复可以修复的问题,并为其他问题插入禁用注释
protolint lint -fix -auto_disable=next .
方法 3: 使用命令行参数
某些规则可以通过命令行参数调整,例如:
# 查看帮助
protolint lint --help
配置路径
protolint 配置文件应放在 protocol/.protolint.yaml 或项目根目录的 .protolint.yaml。
基本用法:
# 在 protocol 目录下运行
cd protocol
protolint lint .
# 在项目根目录运行,指定配置目录
protolint lint -config_dir_path protocol protocol/
# 指定配置文件路径
protolint lint -config_path protocol/.protolint.yaml protocol/mesh/protocol/route_registry.proto
自动修复
# 自动修复一些问题
protolint lint -fix .
# 自动修复并插入禁用注释(推荐,保持兼容性)
protolint lint -fix -auto_disable=next .
Installation
- Via Homebrew
protolintcan be installed for Mac or Linux using Homebrew via the yoheimuta/protolint tap.
brew tap yoheimuta/protolint
brew install protolint
- Via GitHub Releases
- You can also download a pre-built binary from this release page: https://github.com/yoheimuta/protolint/releases
- In the downloads section of each release, you can find pre-built binaries in
.tar.gz packages.
- Use the maintained Docker image
- protolint ships a Docker image yoheimuta/protolint that allows you to use protolint as part of your Docker workflow.
❯❯❯ docker run --volume "$(pwd):/workspace" --workdir /workspace yoheimuta/protolint lint _example/proto
[_example/proto/invalidFileName.proto:1:1] File name should be lower_snake_case.proto.
[_example/proto/issue_88/oneof_options.proto:11:5] Found an incorrect indentation style " ". " " is correct.
[_example/proto/issue_88/oneof_options.proto:12:5] Found an incorrect indentation style " ". " " is correct.
- From Source
- The binary can be installed from source if Go is available. However, I recommend using one of the pre-built binaries instead because it doesn’t include the version info.
go install github.com/yoheimuta/protolint/cmd/protolint@latest
- Within
JavaScript/TypeScript- You can use protolint using your nodejs package manager like
npmoryarn.
- You can use protolint using your nodejs package manager like
$ npm install protolint --save-dev
This will add a reference to a development dependency to your local package.json.
- Within Python projects
- You can use
protolintas a linter within your python projects, the wheelprotolint-binon pypi contains the pre-compiled binaries for various platforms. Just add the desired version to yourpyproject.tomlorrequirements.txt. - The wheels downloaded will contain the compiled go binaries for
protolintandprotoc-gen-protolint. Your platform must be compatible with the supported binary platforms. - You can add the linter configuration to the
tools.protolintpackage inpyproject.toml.
- You can use
Usage
protolint does not require configuration by default, for the majority of projects it should work out of the box.
protolint lint example.proto example2.proto # file mode, specify multiple specific files
protolint lint . # directory mode, search for all .proto files recursively
protolint . # same as "protolint lint ."
protolint lint -config_path=path/to/your_protolint.yaml . # use path/to/your_protolint.yaml
protolint lint -config_dir_path=path/to . # search path/to for .protolint.yaml
protolint lint -fix . # automatically fix some of the problems reported by some rules
protolint lint -fix -auto_disable=next . # this is preferable when you want to fix problems while maintaining the compatibility. Automatically fix some problems and insert disable comments to the other problems. The available values are next and this.
protolint lint -auto_disable=next . # automatically insert disable comments to the other problems.
protolint lint -v . # with verbose output to investigate the parsing error
protolint lint -no-error-on-unmatched-pattern . # exits with success code even if no file is found (file & directory mode)
protolint lint -reporter junit . # output results in JUnit XML format
protolint lint -output_file=path/to/out.txt # output results to path/to/out.txt
protolint lint -plugin ./my_custom_rule1 -plugin ./my_custom_rule2 . # run custom lint rules.
protolint list # list all current lint rules being used
protolint version # print protolint version
protolint --version # print protolint version (global flag)
protolint -v # print protolint version (when used as the only argument)
Version Control Integration
protolint is available as a pre-commit hook. Add this to your .pre-commit-config.yaml in your repository to run protolint with Go:
repos:
- repo: https://github.com/yoheimuta/protolint
rev: v0.56.3 # Select a release here
hooks:
- id: protolint
For Docker-based execution, use the protolint-docker hook:
repos:
- repo: https://github.com/yoheimuta/protolint
hooks:
- id: protolint-docker # Uses yoheimuta/protolint:latest by default
Editor Integration
- Visual Studio Code
- JetBrains IntelliJ IDEA, GoLand, WebStorm, PHPStorm, PyCharm…
Call from Go code
You can also use protolint from Go code. See Go Documentation and lib/lint_test.go in detail.
import (
"bytes"
"github.com/yoheimuta/protolint/lib"
)
func main() {
args := []string{"-config_path", "path/to/your_protolint.yaml", "."}
var stdout bytes.Buffer
var stderr bytes.Buffer
err := lib.Lint(args, &stdout, &stderr)
if err != nil {
// Handle error
}
// Process output in stdout and stderr
}
Rules
See internal/addon/rules in detail.
The rule set follows:
- Official Style Guide. This is enabled by default. Basically, these rules can fix the violations by appending
-fixoption. - Unofficial Style Guide. This is disabled by default. You can enable each rule with
.protolint.yaml.
The -fix option on the command line can automatically fix all the problems reported by fixable rules. See Fixable columns below.
The -auto_disable option on the command line can automatically disable all the problems reported by auto-disable rules. This feature is helpful when fixing the existing violations breaks the compatibility. See AutoDisable columns below.
I recommend that you add
all_default: true in.protolint.yaml, because all linters above are automatically enabled so that you can always enjoy maximum benefits whenever protolint is updated.
Run protolint list to see all available rules.
$ protolint list
FILE_HAS_COMMENT: Verifies that a file starts with a doc comment.
SYNTAX_CONSISTENT: Verifies that syntax is a specified version(default is proto3).
FILE_NAMES_LOWER_SNAKE_CASE: Verifies that all file names are lower_snake_case.proto.
QUOTE_CONSISTENT: Verifies that the use of quote for strings is consistent.
ORDER: Verifies that all files should be ordered in the specific manner.
INDENT: Enforces a consistent indentation style.
MAX_LINE_LENGTH: Enforces a maximum line length.
PACKAGE_NAME_LOWER_CASE: Verifies that the package name doesn't contain any uppercase letters.
IMPORTS_SORTED: Enforces sorted imports.
ENUM_FIELD_NAMES_PREFIX: Verifies that enum field names are prefixed with its ENUM_NAME_UPPER_SNAKE_CASE.
ENUM_FIELD_NAMES_UPPER_SNAKE_CASE: Verifies that all enum field names are CAPITALS_WITH_UNDERSCORES.
ENUM_FIELD_NAMES_ZERO_VALUE_END_WITH: Verifies that the zero value enum should have the suffix (e.g. "UNSPECIFIED", "INVALID").
ENUM_FIELDS_HAVE_COMMENT: Verifies that all enum fields have a comment.
ENUM_NAMES_UPPER_CAMEL_CASE: Verifies that all enum names are CamelCase (with an initial capital).
ENUMS_HAVE_COMMENT: Verifies that all enums have a comment.
FIELD_NAMES_LOWER_SNAKE_CASE: Verifies that all field names are underscore_separated_names.
FIELD_NAMES_EXCLUDE_PREPOSITIONS: Verifies that all field names don't include prepositions (e.g. "for", "during", "at").
FIELDS_HAVE_COMMENT: Verifies that all fields have a comment.
PROTO3_FIELDS_AVOID_REQUIRED: Verifies that all fields should avoid required for proto3.
PROTO3_GROUPS_AVOID: Verifies that all groups should be avoided for proto3.
REPEATED_FIELD_NAMES_PLURALIZED: Verifies that repeated field names are pluralized names.
MESSAGE_NAMES_UPPER_CAMEL_CASE: Verifies that all message names are CamelCase (with an initial capital).
MESSAGE_NAMES_EXCLUDE_PREPOSITIONS: Verifies that all message names don't include prepositions (e.g. "With", "For").
MESSAGES_HAVE_COMMENT: Verifies that all messages have a comment.
RPC_NAMES_UPPER_CAMEL_CASE: Verifies that all rpc names are CamelCase (with an initial capital).
RPC_NAMES_CASE: Verifies that all rpc names conform to the specified convention.
RPCS_HAVE_COMMENT: Verifies that all rpcs have a comment.
SERVICE_NAMES_UPPER_CAMEL_CASE: Verifies that all service names are CamelCase (with an initial capital).
SERVICE_NAMES_END_WITH: Verifies that all service names end with the specified value.
SERVICES_HAVE_COMMENT: Verifies that all services have a comment.
FIELD_NUMBERS_ORDER_ASCENDING: Verifies the order of fields.
Examples
Here are some examples that show good style enabled by default. - is a bad style, + is a good style:
ENUM_FIELD_NAMES_PREFIX
enum FooBar {
- UNSPECIFIED = 0;
+ FOO_BAR_UNSPECIFIED = 0;
}
ENUM_FIELD_NAMES_UPPER_SNAKE_CASE
enum Foo {
- firstValue = 0;
+ FIRST_VALUE = 0;
- second_value = 1;
+ SECOND_VALUE = 1;
}
ENUM_FIELD_NAMES_ZERO_VALUE_END_WITH
enum Foo {
- FOO_FIRST = 0;
+ FOO_UNSPECIFIED = 0;
}
参考:https://github.com/yoheimuta/protolint/issues/256
ENUM_FIELD_NAMES_ZERO_VALUE_END_WITH conforms to the style guide.
The zero value enum should have the suffix `UNSPECIFIED`.
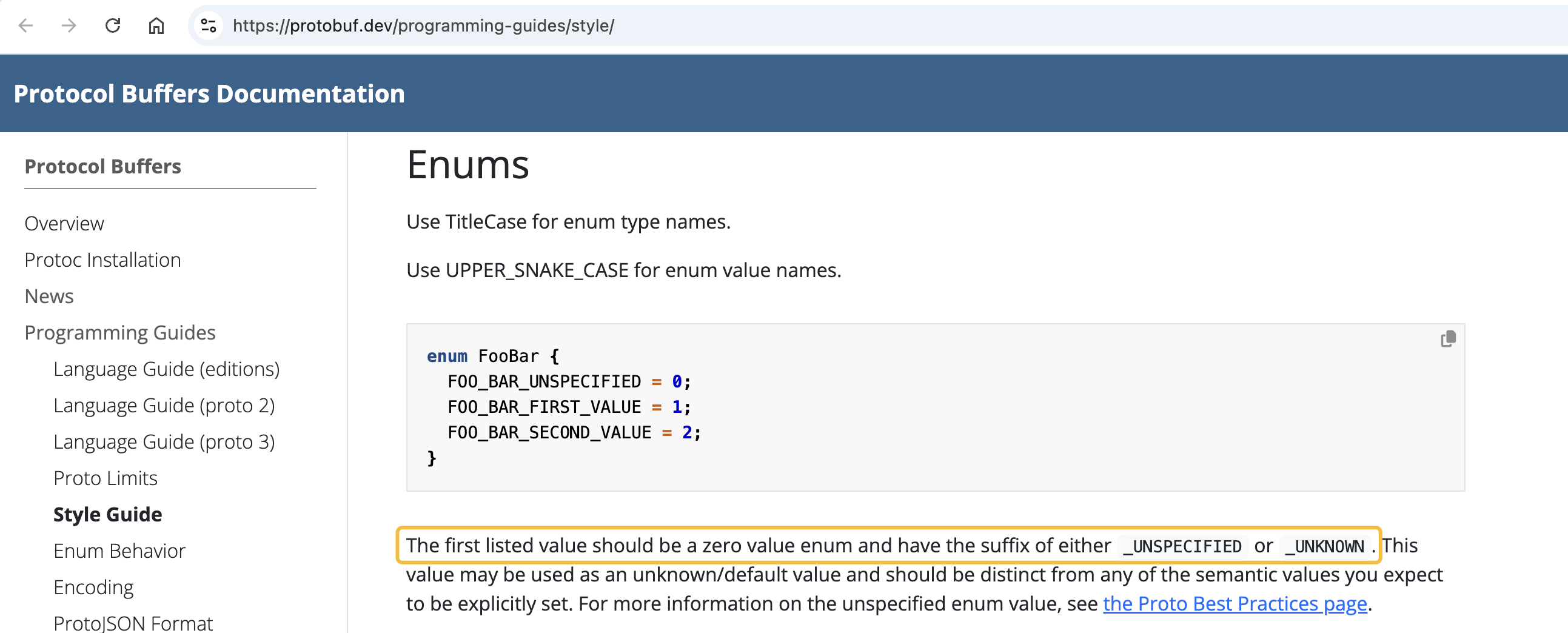
ENUM_NAMES_UPPER_CAMEL_CASE
- enum foobar {
+ enum FooBar {
FIRST_VALUE = 0;
SECOND_VALUE = 1;
}
FIELD_NAMES_LOWER_SNAKE_CASE
message SongServerRequest {
- required string SongName = 1;
+ required string song_name = 1;
}
IMPORTS_SORTED
- import public "new.proto";
+ import "myproject/other_protos.proto";
- import "myproject/other_protos.proto";
+ import public "new.proto";
import "google/protobuf/empty.proto";
import "google/protobuf/timestamp.proto";
MESSAGE_NAMES_UPPER_CAMEL_CASE
- message song_server_request {
+ message SongServerRequest {
required string SongName = 1;
required string song_name = 1;
}
ORDER
- option java_package = "com.example.foo";
- syntax = "proto3";
- package examplePb;
- message song_server_request { }
- import "other.proto";
+ syntax = "proto3";
+ package examplePb;
+ import "other.proto";
+ option java_package = "com.example.foo";
+ message song_server_request { }
PACKAGE_NAME_LOWER_CASE
- package myPackage
+ package my.package
RPC_NAMES_UPPER_CAMEL_CASE
service FooService {
- rpc get_something(FooRequest) returns (FooResponse);
+ rpc GetSomething(FooRequest) returns (FooResponse);
}
RPC_SERVICES_UPPER_CAMEL_CASE
- service foo_service {
+ service FooService {
rpc get_something(FooRequest) returns (FooResponse);
rpc GetSomething(FooRequest) returns (FooResponse);
}
REPEATED_FIELD_NAMES_PLURALIZED
- repeated string song_name = 1;
+ repeated string song_names = 1;
INDENT
enum enumAllowingAlias {
UNKNOWN = 0;
- option allow_alias = true;
+ option allow_alias = true;
STARTED = 1;
- RUNNING = 2 [(custom_option) = "hello world"];
+ RUNNING = 2 [(custom_option) = "hello world"];
- }
+}
- message TestMessage { string test_field = 1; }
+ message TestMessage {
+ string test_field = 1;
+}
QUOTE_CONSISTENT
option java_package = "com.example.foo";
- option go_package = 'example';
+ option go_package = "example";
Creating your custom rules
protolint is the pluggable linter so that you can freely create custom lint rules.
A complete sample project (aka plugin) is included in this repo under the _example/plugin directory.
Reporters
protolint comes with several built-in reporters(aka. formatters) to control the appearance of the linting results.
You can specify a reporter using the -reporter flag on the command line. For example, -reporter junit uses the junit reporter.
The built-in reporter options are:
- plain (default)
- junit
- json
- sarif
- sonar (SonarQube generic issue format)
- unix
- tsc (compatible to TypeScript compiler)
Configure
Disable rules in a Protocol Buffer file
Rules can be disabled with a comment inside a Protocol Buffer file with the following format. The rules will be disabled until the end of the file or until the linter sees a matching enable comment:
// protolint:disable <ruleID1> [<ruleID2> <ruleID3>...]
...
// protolint:enable <ruleID1> [<ruleID2> <ruleID3>...]
It’s also possible to modify a disable command by appending :next or :this for only applying the command to this(current) or the next line respectively.
For example:
enum Foo {
// protolint:disable:next ENUM_FIELD_NAMES_UPPER_SNAKE_CASE
firstValue = 0; // no error
second_value = 1; // protolint:disable:this ENUM_FIELD_NAMES_UPPER_SNAKE_CASE
THIRD_VALUE = 2; // spits out an error
}
Setting the command-line option -auto_disable to next or this inserts disable commands whenever spotting problems.
You can specify -fix option together. The rules supporting auto_disable suppress the violations instead of fixing them that cause a schema incompatibility.
Config file
protolint can operate using a config file named .protolint.yaml.
Refer to _example/config/.protolint.yaml for the config file specification.
protolint will automatically search a current working directory for the config file by default and successive parent directories all the way up to the root directory of the filesystem. And it can search the specified directory with -config_dir_path flag. It can also search the specified file with --config_path flag.
---
# Lint directives.
lint:
# Linter files to ignore.
ignores:
- id: MESSAGE_NAMES_UPPER_CAMEL_CASE
files:
# NOTE: UNIX paths will be properly accepted by both UNIX and Windows.
- _example/proto/simple.proto
- id: ENUM_NAMES_UPPER_CAMEL_CASE
files:
- path/to/foo.proto
# Linter files to walk.
files:
# The specific files to exclude.
exclude:
# NOTE: UNIX paths will be properly accepted by both UNIX and Windows.
- path/to/file
# Linter directories to walk.
directories:
# The specific directories to exclude.
exclude:
# NOTE: UNIX paths will be properly accepted by both UNIX and Windows.
- path/to/dir
# Linter rules.
# Run `protolint list` to see all available rules.
rules:
# Determines whether or not to include the default set of linters.
no_default: true
# Set the default to all linters. This option works the other way around as no_default does.
# If you want to enable this option, delete the comment out below and no_default.
# all_default: true
# The specific linters to add.
add:
- FIELD_NAMES_LOWER_SNAKE_CASE
- MESSAGE_NAMES_UPPER_CAMEL_CASE
- MAX_LINE_LENGTH
- INDENT
- SERVICE_NAMES_END_WITH
- FIELD_NAMES_EXCLUDE_PREPOSITIONS
- MESSAGE_NAMES_EXCLUDE_PREPOSITIONS
- FILE_NAMES_LOWER_SNAKE_CASE
- IMPORTS_SORTED
- PACKAGE_NAME_LOWER_CASE
- ORDER
- MESSAGES_HAVE_COMMENT
- SERVICES_HAVE_COMMENT
- RPCS_HAVE_COMMENT
- FIELDS_HAVE_COMMENT
- PROTO3_FIELDS_AVOID_REQUIRED
- PROTO3_GROUPS_AVOID
- REPEATED_FIELD_NAMES_PLURALIZED
- ENUMS_HAVE_COMMENT
- ENUM_FIELDS_HAVE_COMMENT
- SYNTAX_CONSISTENT
- RPC_NAMES_CASE
- FILE_HAS_COMMENT
- QUOTE_CONSISTENT
- FIELD_NUMBERS_ORDER_ASCENDING
# The specific linters to remove.
remove:
- RPC_NAMES_UPPER_CAMEL_CASE
# Linter rules option.
rules_option:
# MAX_LINE_LENGTH rule option.
max_line_length:
# Enforces a maximum line length
max_chars: 80
# Specifies the character count for tab characters
tab_chars: 2
# INDENT rule option.
indent:
# Available styles are 4(4-spaces), 2(2-spaces) or tab.
style: 4
# Specifies if it should stop considering and inserting new lines at the appropriate positions
# when the inner elements are on the same line. Default is false.
not_insert_newline: true
# FILE_NAMES_LOWER_SNAKE_CASE rule option.
file_names_lower_snake_case:
excludes:
- ../proto/invalidFileName.proto
# QUOTE_CONSISTENT rule option.
quote_consistent:
# Available quote are "double" or "single".
quote: double
# ENUM_FIELD_NAMES_ZERO_VALUE_END_WITH rule option.
enum_field_names_zero_value_end_with:
suffix: INVALID
# SERVICE_NAMES_END_WITH rule option.
service_names_end_with:
text: Service
# FIELD_NAMES_EXCLUDE_PREPOSITIONS rule option.
field_names_exclude_prepositions:
# The specific prepositions to determine if the field name includes.
prepositions:
- for
- at
- of
# The specific keywords including prepositions to ignore. E.g. end_of_support is a term you would like to use, and skip checking.
excludes:
- end_of_support
# REPEATED_FIELD_NAMES_PLURALIZED rule option.
## The spec for each rules follows the implementation of https://github.com/gertd/go-pluralize.
## Plus, you can refer to this rule's test code.
repeated_field_names_pluralized:
uncountable_rules:
- paper
irregular_rules:
Irregular: Regular
# MESSAGE_NAMES_EXCLUDE_PREPOSITIONS rule option.
message_names_exclude_prepositions:
# The specific prepositions to determine if the message name includes.
prepositions:
- With
- For
- Of
# The specific keywords including prepositions to ignore. E.g. EndOfSupport is a term you would like to use, and skip checking.
excludes:
- EndOfSupport
-
# RPC_NAMES_CASE rule option.
rpc_names_case:
# The specific convention the name should conforms to.
## Available conventions are "lower_camel_case", "upper_snake_case", or "lower_snake_case".
convention: upper_snake_case
# MESSAGES_HAVE_COMMENT rule option.
messages_have_comment:
# Comments need to begin with the name of the thing being described. default is false.
should_follow_golang_style: true
# SERVICES_HAVE_COMMENT rule option.
services_have_comment:
# Comments need to begin with the name of the thing being described. default is false.
should_follow_golang_style: true
# RPCS_HAVE_COMMENT rule option.
rpcs_have_comment:
# Comments need to begin with the name of the thing being described. default is false.
should_follow_golang_style: true
# FIELDS_HAVE_COMMENT rule option.
fields_have_comment:
# Comments need to begin with the name of the thing being described. default is false.
should_follow_golang_style: true
# ENUMS_HAVE_COMMENT rule option.
enums_have_comment:
# Comments need to begin with the name of the thing being described. default is false.
should_follow_golang_style: true
# ENUM_FIELDS_HAVE_COMMENT rule option.
enum_fields_have_comment:
# Comments need to begin with the name of the thing being described. default is false.
should_follow_golang_style: true
# SYNTAX_CONSISTENT rule option.
syntax_consistent:
# Default is proto3.
version: proto2
Exit codes
When linting files, protolint will exit with one of the following exit codes:
0: Linting was successful and there are no linting errors.1: Linting was successful and there is at least one linting error.2: Linting was unsuccessful due to all other errors, such as parsing, internal, and runtime errors.
Refer
- https://github.com/yoheimuta/protolint
- Style Guide
- Language Guide (proto3)
- Language Guide (proto2)
- Tutorials