Redis 5.0.0 in Action
- 数据库对比
- Redis初步
- Redis代码结构
- 数据类型
- 执行命令
- Lua scripts server
- Pub-Sub server
- Redis的事务
- Redis键的过期时间
- Redis的持久化
- Redis的复制
- Redis的性能
- Redis的应用
- 数据同步
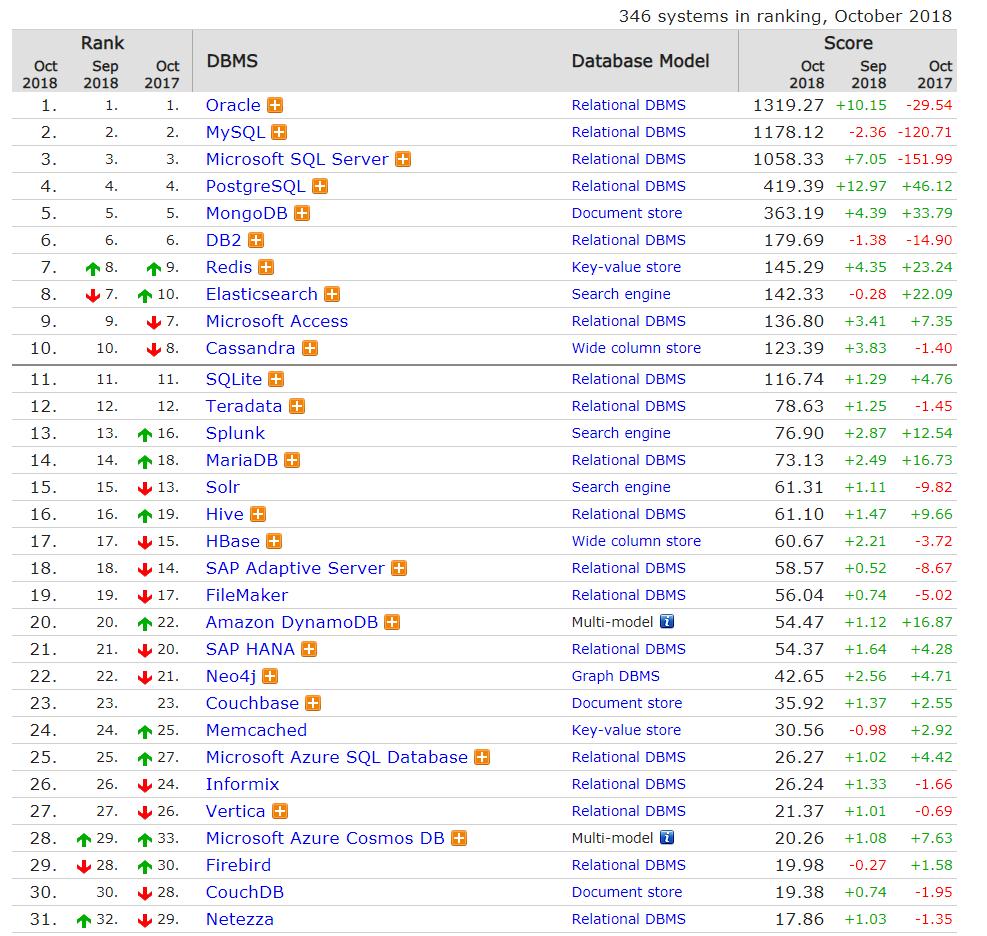
一提起数据库,大多数人可能想到的是Oracle,MySQL以及Microsoft SQL Server这三大巨头。但除此外,很多新兴的数据库也开始被开发者使用。例如,基于海量日志查询的Elasticsearch,在高并发场景使用Redis做缓存。DB-engines上可以看到近期数据库的使用排名情况。可以看到Redis作为一款NoSQL数据库(非关系型数据库)其排名正处在一个上升的阶段。Redis使用ANSI C编写,目前是一位意大利的开发者Salvatore Sanfilippo来维护,他在twitter上非常活跃,可以帮助开发者了解更多最新的Redis信息,也可订阅官方的Redis邮件组。可以在GitHub上找到最新的Redis源码,也有一个Redis在线测试工具可以尝试Redis的一些基本用法。在了解完Redis之后,思考问题的方式也会发生改变,从原来怎样将数据塞到数据库表里,变为应该使用哪种Redis的数据结构来解决这个问题。
关于使用Cache的一个有趣的故事:TutorialCachingStory
数据库对比
| 名称 | 类型 | 数据存储选项 | 查询类型 | 附加功能 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Redis | 使用内存存储(in-memory)的非关系数据库 | 字符串、列表、集合、散列表、有序集合 | 每种数据类型都有自己的专属命令,另外还有批量操作(bulk operation)和不完全(partial)的事务支持 | 发布与订阅,主从复制,持久化,存储过程 |
| memcached | 使用内存存储的键值缓存 | 键值之间的映射 | 创建命令、读取命令、更新命令、删除命令以及其他几个命令 | 为提升性能而设的多线程服务器 |
| MySQL | 关系数据库 | 每个数据库可以包含多个表,每个表可以包含多个行,可以处理多个表的视图(view),支持空间(spatial)和第三方扩展 | SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, 函数, 存储过程 | 支持ACID性质(需要使用InnoDB),主从复制,主主复制 |
| PostgreSQL | 关系数据库 | 基本同MySQL | 基本同MySQL | 支持ACID性质,主从复制,由第三方支持的多主复制 |
| MongoDB | 使用硬盘存储(on-disk)的非关系文档存储 | 每个数据库可以包含多个表,每个表可以包含多个schema-less的BSON文档 | 创建命令,读取命令,更新命令,删除命令,条件查询命令等 | 支持map-reduce操作,主从复制,分片,空间索引(spatial index) |
Redis是一个支持网络,以键值对的形式存储数据,可基于内存亦可持久性的开源数据库。从数据库的类型分类来说,Redis有别于传统关系型数据库(如Oracle,MySQL)的表结构,也与其他NoSQL(如Neo4j,MongoDB等)有本质的区别。常与Redis进行比较的数据库是Memcached,两者都是存储键值对,但在底层实现上却有较大的不同。
-
Redis存储的value类型相对来说比memcached多。Redis支持二进制案例的 Strings(字符串), Lists(链表), Hashes(哈希类型), Sets (集合)及 Sorted Sets(有序集合)等数据类型的操作。在有序集合上面,redis还支持各种不同方式的排序。
-
基于内存,并具备自动写入磁盘功能,性能极高。Redis能支持超过 100K+ 每秒的读写频率。这得益于Redis把数据缓存在内存中。这一点与memcached较为相似,但两者区别在于,Redis会周期性地把更新的数据写入磁盘或者把修改操作写入追加的记录文件,并且在此基础上实现了master-slave(主从)同步。也就是说,数据可以由主服务器向任意数量的从服务器上同步。
-
原子性操作,保证数据的一致性。Redis提供了push/pop、add/remove及取交集并集和差集及更丰富的数据操作,然而这些操作都是原子性的,保证了操作前后数据的一致性。此外,Redis还支持对几个操作合并后的原子性执行。
-
其他丰富特性。Redis还支持 publish/subscribe, 通知, key 过期等等特性。Redis提供了Java,C/C++,C#,PHP,JavaScript,Perl,Object-C,Python,Ruby等客户端,使用很方便。
Redis在数据库的可用性,可扩展性和可维护性上都表现出较高的性能,因而能在数据库大家族,尤其是NoSQL中占据一席之地。
Redis初步
Redis is an open source (BSD licensed), in-memory data structure store, used as a database, cache and message broker. It supports data structures such as strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets with range queries, bitmaps, hyperloglogs and geospatial indexes with radius queries. Redis has built-in replication, Lua scripting, LRU eviction, transactions and different levels of on-disk persistence, and provides high availability via Redis Sentinel and automatic partitioning with Redis Cluster.
可以将Redis视为一个复杂的Memcached,因为Redis支持更多的数据类型操作。
- Redis可以存储key与5种不同类型的value之间的映射
- Redis可以将存储在内存的键值对数据持久化到硬盘
- Redis可以使用复制特性来扩展读性能
- Redis可以使用客户端分片来扩展写性能
分片是一种将数据划分为多个部分的方法,对数据的划分可以基于键包含的ID、基于键的散列值、或者基于以上两者的某种组合。通过对数据进行分片,用户可以将数据存储到多台机器里面,也可以从多台机器里面获取数据,这种方法在解决某些问题时可以获得线性级别的性能提升。
- Redis有两种不同的
持久化方法。一种是时间点转储(point-in-time dump),第二种是将所有修改了数据库的命令都写入一个只追加(append-only)文件里面 - Redis通过主从复制,来提供故障转移(failover)支持。执行复制的从服务器会连接上主服务器,接收主服务器发送的整个数据库的初始副本,然后主服务器执行的
写命令,都会发送给所有连着的从服务器去执行,从而实时地更新从服务器的数据集。因此,客户端可以读任意一台Redis集群的机器获取数据。(即,强同步的方式) -
使用Redis一般是基于性能(通过内存操作,避免对磁盘的随机读或者随机写)或者功能(比如,使用Redis可以将聚合数据放到有序集合
ZSET里面,构建出一个实时的排行榜)的考虑,如果因为费用原因而没办法将大量数据存储到内存里面,则会选择关系数据库 - 当前最新稳定的版本是[Redis 5.0.0(Released Wed Oct 17 13:28:26 CEST 2018)]
- 通过README可以快速了解其基本用法
- 支持的平台包括,Linux, OSX, OpenBSD, NetBSD, FreeBSD
- Redis的安装
- 从 http://redis.io/download下载最新的stable版本的源码
- 编译(如果要查看详细的编译过程,可以指定
make V=1),安装和启动Redis - 下载并安装Python语言的Redis客户端库,或者使用自带的客户端测试工具
- Redis在
deps目录下是对外部第三方库的依赖包括,jemalloc, lua, hiredis, linenoise,如果要重新编译第三方库需要先执行make distclean,默认不会编译 - Redis在Linux下默认使用jemalloc,而在其他环境下默认使用libc malloc。jemalloc相比libc malloc对内存碎片问题处理的更好。通过
MALLOC环境变量指定使用哪种内存分配器。
make MALLOC=jemalloc
make MALLOC=libc
- 运行Redis的方式,所有redis.conf配置中的选项,也支持在命令行指定
cd src
./redis-server
./redis-server /path/to/redis.conf
./redis-server --port 9999 --replicaof 127.0.0.1 6379
./redis-server /etc/redis/6379.conf --loglevel debug
- 编译后安装Redis的bin文件,不包括
初始化脚本和配置文件
make install # /usr/local/bin
make PREFIX=/some/other/directory install
对于生产环境的部署,如果是Ubuntu或者Debian系统,可以参考以下脚本
cd utils
./install_server.sh
- 对Redis实例的起停
/etc/init.d/redis_<portnumber>
/etc/init.d/redis_6379
redis-cli shutdown
Redis代码结构
| 目录 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| src | contains the Redis implementation, written in C |
| tests | contains the unit tests, implemented in Tcl |
| deps | contains libraries Redis uses |
| utils | |
| some files | Makefile/README.md/redis.conf/sentinel.conf/… |
关于deps目录的补充说明:
- Everything needed to compile Redis is inside this directory; your system just needs to provide
libc,a POSIX compatible interfaceanda C compiler. - Notably deps contains a copy of
jemalloc, which is the default allocator of Redis under Linux. - Note that under deps there are also things which started with the Redis project, but for which the main repository is not antirez/redis. An exception to this rule is deps/geohash-int which is the low level geocoding library used by Redis: it originated from a different project, but at this point it diverged so much that it is developed as a separated entity directly inside the Redis repository.
src/server.h
Redis的所有配置和一些状态信息,全部记录在struct redisServer结构里。
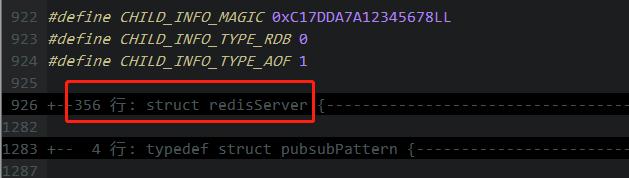
struct redisServer {
/* General */
pid_t pid; /* Main process pid. */
char *configfile; /* Absolute config file path, or NULL */
char *executable; /* Absolute executable file path. */
char **exec_argv; /* Executable argv vector (copy). */
int dynamic_hz; /* Change hz value depending on # of clients. */
int config_hz; /* Configured HZ value. May be different than
the actual 'hz' field value if dynamic-hz
is enabled. */
// ...
};
需要关心的几个重要结构包括:
server.db
redisDb *db;
/* Redis database representation. There are multiple databases identified
* by integers from 0 (the default database) up to the max configured
* database. The database number is the 'id' field in the structure. */
typedef struct redisDb {
dict *dict; /* The keyspace for this DB */
dict *expires; /* Timeout of keys with a timeout set */
dict *blocking_keys; /* Keys with clients waiting for data (BLPOP)*/
dict *ready_keys; /* Blocked keys that received a PUSH */
dict *watched_keys; /* WATCHED keys for MULTI/EXEC CAS */
int id; /* Database ID */
long long avg_ttl; /* Average TTL, just for stats */
list *defrag_later; /* List of key names to attempt to defrag one by one, gradually. */
} redisDb;
server.commands
dict *commands; /* Command table */
// src/dict.h
// Hash Tables Implementation
/* This is our hash table structure. Every dictionary has two of this as we
* implement incremental rehashing, for the old to the new table. */
typedef struct dictht {
dictEntry **table;
unsigned long size;
unsigned long sizemask;
unsigned long used;
} dictht;
typedef struct dict {
dictType *type;
void *privdata;
dictht ht[2];
long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */
unsigned long iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */
} dict;
server.clients
记录客户端的连接。(a linked list of clients connected to the server)
list *clients; /* List of active clients */
server.master
a special client, the master, if the instance is a replica.
client *master; /* Client that is master for this slave */
client
// src/server.h
/* With multiplexing we need to take per-client state.
* Clients are taken in a linked list. */
struct client {
int fd;
sds querybuf;
int argc;
robj **argv;
redisDb *db;
int flags;
list *reply;
char buf[PROTO_REPLY_CHUNK_BYTES];
... many other fields ...
}
- The
fdfield is the client socket file descriptor. argcandargvare populated with the command the client is executing, so that functions implementing a given Redis command can read the arguments.querybufaccumulates the requests from the client, which are parsed by the Redis server according to the Redis protocol and executed by calling the implementations of the commands the client is executing.replyandbufare dynamic and static buffers that accumulate the replies the server sends to the client. These buffers are incrementally written to the socket as soon as the file descriptor is writable.
redisObject
struct redisObject可以表示Redis的所有基本类型,例如,strings, lists, sets, sorted sets等- 通过
type字段,区分实际表示哪类对象 - 并通过
refcount字段实现引用计数,防止对象的多次创建
#define LRU_BITS 24
typedef struct redisObject {
unsigned type:4;
unsigned encoding:4;
unsigned lru:LRU_BITS; /* LRU time (relative to global lru_clock) or
* LFU data (least significant 8 bits frequency
* and most significant 16 bits access time). */
int refcount;
void *ptr;
} robj;
src/server.c
主流程
Redis server的入口main()函数在此文件定义,可以了解到Redis内部是如何启动的。
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
// ...
// setups the default values of the server structure
initServerConfig();
// allocates the data structures needed to operate, setup the listening socket, and so forth
initServer();
// starts the event loop which listens for new connections
aeMain(server.el);
}
周期性任务
有两个特殊的函数,在event loop中被周期地调用。
serverCron()is called periodically (according toserver.hzfrequency), and performs tasks that must be performed from time to time, like checking for timedout clients.beforeSleep()is called every time the event loop fired, Redis served a few requests, and is returning back into the event loop.
/* This is our timer interrupt, called server.hz times per second.
* Here is where we do a number of things that need to be done asynchronously.
* For instance:
*
* - Active expired keys collection (it is also performed in a lazy way on
* lookup).
* - Software watchdog.
* - Update some statistic.
* - Incremental rehashing of the DBs hash tables.
* - Triggering BGSAVE / AOF rewrite, and handling of terminated children.
* - Clients timeout of different kinds.
* - Replication reconnection.
* - Many more...
*
* Everything directly called here will be called server.hz times per second,
* so in order to throttle execution of things we want to do less frequently
* a macro is used: run_with_period(milliseconds) { .... }
*/
int serverCron(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long id, void *clientData)
/* This function gets called every time Redis is entering the
* main loop of the event driven library, that is, before to sleep
* for ready file descriptors. */
void beforeSleep(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop);
其他重要功能
call()is used in order to call a given command in the context of a given client.activeExpireCycle()handles eviciton of keys with a time to live set via theEXPIREcommand.freeMemoryIfNeeded()is called when a new write command should be performed but Redis is out of memory according to themaxmemorydirective.- The global variable
redisCommandTabledefines all the Redis commands, specifying the name of the command, the function implementing the command, the number of arguments required, and other properties of each command.
/* Call() is the core of Redis execution of a command.
*
* The following flags can be passed:
* CMD_CALL_NONE No flags.
* CMD_CALL_SLOWLOG Check command speed and log in the slow log if needed.
* CMD_CALL_STATS Populate command stats.
* CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_AOF Append command to AOF if it modified the dataset
* or if the client flags are forcing propagation.
* CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_REPL Send command to salves if it modified the dataset
* or if the client flags are forcing propagation.
* CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE Alias for PROPAGATE_AOF|PROPAGATE_REPL.
* CMD_CALL_FULL Alias for SLOWLOG|STATS|PROPAGATE.
*
* The exact propagation behavior depends on the client flags.
* Specifically:
*
* 1. If the client flags CLIENT_FORCE_AOF or CLIENT_FORCE_REPL are set
* and assuming the corresponding CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_AOF/REPL is set
* in the call flags, then the command is propagated even if the
* dataset was not affected by the command.
* 2. If the client flags CLIENT_PREVENT_REPL_PROP or CLIENT_PREVENT_AOF_PROP
* are set, the propagation into AOF or to slaves is not performed even
* if the command modified the dataset.
*
* Note that regardless of the client flags, if CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_AOF
* or CMD_CALL_PROPAGATE_REPL are not set, then respectively AOF or
* slaves propagation will never occur.
*
* Client flags are modified by the implementation of a given command
* using the following API:
*
* forceCommandPropagation(client *c, int flags);
* preventCommandPropagation(client *c);
* preventCommandAOF(client *c);
* preventCommandReplication(client *c);
*
*/
void call(client *c, int flags);
/* Try to expire a few timed out keys. The algorithm used is adaptive and
* will use few CPU cycles if there are few expiring keys, otherwise
* it will get more aggressive to avoid that too much memory is used by
* keys that can be removed from the keyspace.
*
* No more than CRON_DBS_PER_CALL databases are tested at every
* iteration.
*
* This kind of call is used when Redis detects that timelimit_exit is
* true, so there is more work to do, and we do it more incrementally from
* the beforeSleep() function of the event loop.
*
* Expire cycle type:
*
* If type is ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST the function will try to run a
* "fast" expire cycle that takes no longer than EXPIRE_FAST_CYCLE_DURATION
* microseconds, and is not repeated again before the same amount of time.
*
* If type is ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW, that normal expire cycle is
* executed, where the time limit is a percentage of the REDIS_HZ period
* as specified by the ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC define. */
void activeExpireCycle(int type);
/* This function is periodically called to see if there is memory to free
* according to the current "maxmemory" settings. In case we are over the
* memory limit, the function will try to free some memory to return back
* under the limit.
*
* The function returns C_OK if we are under the memory limit or if we
* were over the limit, but the attempt to free memory was successful.
* Otehrwise if we are over the memory limit, but not enough memory
* was freed to return back under the limit, the function returns C_ERR. */
int freeMemoryIfNeeded(void);
src/networking.c
此文件定义了clients, masters和replicas涉及的网络I/O函数。
createClient()allocates and initializes a new client.- the
addReply*()family of functions are used by commands implementations in order to append data to the client structure, that will be transmitted to the client as a reply for a given command executed. writeToClient()transmits the data pending in the output buffers to the client and is called by the writable event handlersendReplyToClient().readQueryFromClient()is the readable event handler and accumulates data from read from the client into the query buffer.processInputBuffer()is the entry point in order to parse the client query buffer according to the Redis protocol. Once commands are ready to be processed, it callsprocessCommand()which is defined insideserver.cin order to actually execute the command.freeClient()deallocates, disconnects and removes a client.
src/aof.c src/rdb.c
RDB和AOF的持久化(persistence)实现。
Redis uses a persistence model based on the fork() system call in order to create a thread with the same (shared) memory content of the main Redis thread. This secondary thread dumps the content of the memory on disk. This is used by rdb.c to create the snapshots on disk and by aof.c in order to perform the AOF rewrite when the append only file gets too big.
src/db.c
一些通用的命令实现。
lookupKeyRead()andlookupKeyWrite()are used in order to get a pointer to the value associated to a given key, orNULLif the key does not exist.dbAdd()and its higher level counterpartsetKey()create a new key in a Redis database.dbDelete()removes a key and its associated value.emptyDb()removes an entire single database or all the databases defined.
src/object.c
对Redis对象robj的操作接口。
incrRefcount()anddecrRefCount()are used in order to increment or decrement an object reference count. When it drops to 0 the object is finally freed.createObject()allocates a new object. There are also specialized functions to allocate string objects having a specific content, likecreateStringObjectFromLongLong()and similar functions.
src/replication.c
关于数据同步的实现。
One of the most important functions inside this file is replicationFeedSlaves() that writes commands to the clients representing replica instances connected
to our master, so that the replicas can get the writes performed by the clients:
this way their data set will remain synchronized with the one in the master.
Other C files
t_hash.c,t_list.c,t_set.c,t_string.candt_zset.ccontains the implementation of the Redis data types. They implement both an API to access a given data type, and the client commands implementations for these data types.ae.cimplements the Redis event loop, it’s a self contained library which is simple to read and understand.sds.cis the Redis string library, check http://github.com/antirez/sds for more information.anet.cis a library to use POSIX networking in a simpler way compared to the raw interface exposed by the kernel.dict.cis an implementation of a non-blocking hash table which rehashes incrementally.scripting.cimplements Lua scripting. It is completely self contained from the rest of the Redis implementation and is simple enough to understand if you are familar with the Lua API.cluster.cimplements the Redis Cluster. Probably a good read only after being very familiar with the rest of the Redis code base. If you want to readcluster.cmake sure to read the Redis Cluster specification.
数据类型
首先需要了解Redis Data Types有哪些。
Redis提供的5种基本数据结构
| 结构类型 | 结构存储的值 | 结构的读写能力 |
| STRING | 可以是字符串,整数,浮点数 | 可以对整个字符串或者其中一部分执行操作;对整数和浮点数执行自增(increment)或者自减(decrement) |
| LIST | 一个链表,链表上的每个节点都包含了一个字符串 | 从链表的两端推入或者弹出元素;根据偏移量对链表进行修剪(trim);读取单个或者多个元素;根据值查找或者移除元素 |
| SET | 包含字符串的无序收集器(unordered collection),并且被包含的每个字符串都是独一无二,各不相同 | 添加,获取,移除单个元素;检查一个元素是否存在于集合中;计算交集,并集,差集;从集合里面随机获取元素 |
| HASH | 包含键值对的无序散列表 | 添加,获取,删除单个键值对;获取所有键值对 |
| ZSET | 字符串成员与浮点数分值之间的有序映射,元素的排列顺序由分值的大小决定 | 添加,获取,删除单个元素;根据分值范围或者成员来获取元素 |
- Binary-safe strings.
- Lists: collections of string elements sorted according to the order of insertion. They are basically linked lists.
- Sets: collections of unique, unsorted string elements.
- Sorted sets, similar to Sets but where every string element is associated to a floating number value, called score. The elements are always taken sorted by their score, so unlike Sets it is possible to retrieve a range of elements (for example you may ask: give me the top 10, or the bottom 10).
- Hashes, which are maps composed of fields associated with values. Both the field and the value are strings. This is very similar to Ruby or Python hashes.
- Bit arrays (or simply bitmaps): it is possible, using special commands, to handle String values like an array of bits: you can set and clear individual bits, count all the bits set to 1, find the first set or unset bit, and so forth.
- HyperLogLogs: this is a probabilistic data structure which is used in order to estimate the cardinality of a set. Don’t be scared, it is simpler than it seems… See later in the HyperLogLog section of this tutorial.
Redis的键(key)
Redis的key是二级制安全的,使用上对key的几个原则:
- key的长度不建议太长,否则会影响查询效率。对于过长的key可以通过hash的方法减少其长度
- key的长度也不建议太短,否则会影响可读性
- 规定好一种好的格式,比如:
user:1000 - key允许的最大长度是512MB
Redis对key的创建和删除原则:
-
When we add an element to an aggregate data type, if the target key does not exist, an empty aggregate data type is created before adding the element. 当往一个key中添加元素时,若key不存在,Redis会自动先创建key,然后再添加元素。
-
When we remove elements from an aggregate data type, if the value remains empty, the key is automatically destroyed. 当一个key的value为空时,Redis会自动清除这个key。
-
Calling a read-only command such as LLEN (which returns the length of the list), or a write command removing elements, with an empty key, always produces the same result as if the key is holding an empty aggregate type of the type the command expects to find. 此规则与第一条类似。
> del mylist
(integer) 1
> lpush mylist 1 2 3
(integer) 3
> lpush mylist 1 2 3
(integer) 3
> exists mylist
(integer) 1
> lpop mylist
"3"
> lpop mylist
"2"
> lpop mylist
"1"
> exists mylist
(integer) 0
> del mylist
(integer) 0
> llen mylist
(integer) 0
> lpop mylist
(nil)
Redis的值(value)
STRING
Redis最简单的一种值类型,可以用来存储一个网页,或者存储一张照片。其最大长度不能超过512MB。在Redis里面,字符串可以存储以下3种类型的值:
- 字节串
- 整数
- 浮点数
如果尝试对一个值,无法被解释为整数或者浮点数的字符串键执行自增或者自减操作,Redis将返回错误。
基本操作
| 命令 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| SET | 可看做一种赋值操作 |
| SET $key $value nx | 如果key已经存在,不允许覆盖 |
| SET $key $value xx | 如果key已经存在,允许覆盖 |
./redis-cli
127.0.0.1:6379> set mykey
(error) ERR wrong number of arguments for 'set' command
127.0.0.1:6379> set mykey value
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> get mykey
"value"
127.0.0.1:6379> set mykey value2
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> get mykey
"value2"
127.0.0.1:6379> set mykey value3 nx
(nil)
127.0.0.1:6379> get mykey
"value2"
127.0.0.1:6379> set mykey value3 xx
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> get mykey
"value3"
原子操作
| 命令 | 含义 | 应用场景 |
|---|---|---|
| incr | 加 1 | |
| incrby | 加 $n | |
| decr | 减 1 | |
| decrby | 减 $n | |
| getset | 设置新值,并返回老值 | 比如,按周期统计 |
127.0.0.1:6379> set cnt 100
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> incr cnt
(integer) 101
127.0.0.1:6379> incr cnt
(integer) 102
127.0.0.1:6379> incrby cnt 50
(integer) 152
127.0.0.1:6379> decr cnt
(integer) 151
127.0.0.1:6379> decr cnt
(integer) 150
127.0.0.1:6379> decrby cnt 50
(integer) 100
127.0.0.1:6379> get cnt
"100"
127.0.0.1:6379> getset cnt 1
"100"
127.0.0.1:6379> get cnt
"1"
批量操作
批量操作,可以减少交互的延迟。
| 命令 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| mset | 批量设置多个值 |
| mget | 批量获取多个值 |
127.0.0.1:6379> mset a 10 b 20 c 30
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> mget a b c
1) "10"
2) "20"
3) "30"
对key的操作
| 命令 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| exists | 判断某个key是否存在 |
| del | 删除某个key |
| type | 返回某个key对应的value类型 |
127.0.0.1:6379> set mykey hello
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> get mykey
"hello"
127.0.0.1:6379> exists mykey
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> del mykey
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> del mykey
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> get mykey
(nil)
127.0.0.1:6379> exists mykey
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> set mykey hello
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> type mykey
string
127.0.0.1:6379> del mykey
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> type mykey
none
过期操作(expires)
可以对某个key设置一个timeout,超时后会自动del当前的key。过期时间精度支持秒和毫秒。
| 命令 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| expire | 指定某个key的过期时间 |
| set key 100 ex 10 | 通过set选项指定过期时间,指定key 10秒后过期 |
| ttl | 查看某个key过期前的剩余时间 |
| PEXPIRE | 同expire,精度为毫秒 |
| PTTL | 同ttl,精度为毫秒 |
> set key some-value
OK
> expire key 5
(integer) 1
> get key (immediately)
"some-value"
> get key (after some time)
(nil)
> set key 100 ex 10
OK
> ttl key
(integer) 9
LIST
Redis的LIST底层实现为一个链表结构,而不是一个连续的数组。
优点:插入时间复杂度是O(1) 缺点:查询时间复杂度是O(n)
LIST的一个使用场景:例如,当写博客的时候,每次创建新的文章就把文章的ID LPUSH 到一个LIST里,当访问博客的时候,通过LRANGE 0 9只展示最新的10篇文章。
基本操作
| 命令 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| LPUSH | 从左(头部)添加一个元素到链表里 |
| RPUSH | 从右(尾部)添加一个元素到链表里 |
| LRANGE beg_idx end_idx | 从链表获取某个范围的元素,其中,位置索引支持负值。例如,-1表示最后一个元素,-2表示倒数第二个元素。 |
| RPOP | 从右弹出一个元素 |
| LTRIM | 类似LRANGE,区别是只保留指定范围内的元素,其他全部删除(discarded) |
> rpush mylist A
(integer) 1
> rpush mylist B
(integer) 2
> lpush mylist first
(integer) 3
> lrange mylist 0 -1
1) "first"
2) "A"
3) "B"
> rpush mylist 1 2 3 4 5 "foo bar"
(integer) 9
> lrange mylist 0 -1
1) "first"
2) "A"
3) "B"
4) "1"
5) "2"
6) "3"
7) "4"
8) "5"
9) "foo bar"
> rpush mylist a b c
(integer) 3
> rpop mylist
"c"
> rpop mylist
"b"
> rpop mylist
"a"
> rpush mylist 1 2 3 4 5
(integer) 5
> ltrim mylist 0 2
OK
> lrange mylist 0 -1
1) "1"
2) "2"
3) "3"
生产者消费者模型 (基于LIST的阻塞操作)
问题:如果使用LIST正常的接口,实现一个生产者消费者模型如下过程,但是存在一个问题是,如果LIST为空,消费者会通过轮询(polling)的方式重试,会造成对Redis很多无用的操作。
- To push items into the list, producers call
LPUSH. - To extract / process items from the list, consumers call
RPOP.
解决方案:
Redis implements commands called BRPOP and BLPOP which are versions of RPOP and LPOP able to block if the list is empty: they’ll return to the caller only when a new element is added to the list, or when a user-specified timeout is reached.
MORE:
- It is possible to build safer queues or rotating queues using
RPOPLPUSH. - There is also a blocking variant of the command, called
BRPOPLPUSH.
HASH
Redis的散列可以将多个键值对存储到一个键里面,使得散列非常适用于将一些相关的数据存储在一起。可以把这种数据的聚集看做是关系数据库中的行,或者文档数据库中的文档。
| 命令 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| hset | 在hash里设置一个键值对 |
| hget | 在hash里获取一个键值对 |
| hmset | 批量设置多个键值对 |
| hmget | 批量获取多个键值对 |
| hgetall | 获取所有键值对 |
| hkeys | 获取散列包含的所有键 |
| hvals | 获取散列包含的所有值 |
| hexists | 检查给定键是否存在于散列中 |
| hincrby | 可以对hash里,某个键执行incrby操作 |
> hmset user:1000 username antirez birthyear 1977 verified 1
OK
> hget user:1000 username
"antirez"
> hget user:1000 birthyear
"1977"
> hgetall user:1000
1) "username"
2) "antirez"
3) "birthyear"
4) "1977"
5) "verified"
6) "1"
> hmget user:1000 username birthyear no-such-field
1) "antirez"
2) "1977"
3) (nil)
> hincrby user:1000 birthyear 10
(integer) 1987
> hincrby user:1000 birthyear 10
(integer) 1997
SET
Redis的集合,以无序的方式来存储多个不同的元素。
| 命令 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| sadd | 像集合中添加元素 |
| smembers | 返回集合中所有元素 |
| sismember | 检查某个元素是否存在 |
| SPOP | 从集合中随机删除一个元素,并返回客户端 |
| SCARD | 返回集合包含的元素数量 |
用于组合和处理多个集合的命令:
| 命令 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| SDIFF | 返回存在于第一个集合,但不存在于其他集合中的元素,即差集 |
| SINTER | 返回同时存在于所有集合的元素,即交集 |
| SUNION | 返回至少存在于一个集合中的元素,即并集 |
对应于以上三个返回结果的版本,也有三个存储结果的版本,分别是,SDIFFSTORE, SINTERSTORE, SUNIONSTORE。
Sorted SET
和散列存储着键与值之间的映射类似,有序集合也存储着成员与分值之间的映射,并提供了分值的处理命令。这些分值在Redis中以IEEE 754双精度浮点数的格式存储。
比如:
- 实现基于发表时间排序的文章列表
- 基于投票数量排序的文章列表
- 存储cookie的过期时间
| 命令 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| zadd key-name score member [socre member …] | 将带有给定分值的成员添加到有序集合里 |
| zrem key-name member [member …] | 从有序集合里移除给定的成员,并返回被移除成员的数量 |
| zcard key-name | 返回有序集合包含的成员数量 |
| zincrby key-name increment member | 将member成员的分值加上increment |
| zcount key-name min max | 返回分值介于min和max之间的成员数量 |
| zrank key-name member | 返回成员member在有序集合中的排名 |
| zscore key-name member | 返回成员member的分值 |
| zrange key-name start stop [withscores] | 返回有序集合中排名介于start和stop之间的成员,如果给定了可选的withscores选项,那么命令会将成员的分值也一并返回 |
基于返回的获取,删除,以及并集,交集命令。
| 命令 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| ZREVRANK key-name member | 返回有序集合里成员member的排名,成员按照分值从大到小排列 |
| ZREVRANGE key-name start stop [withscores] | 返回有序集合给定排名范围内的成员,成员按照分值从大到小排列 |
| ZRANGEBYSCORE | 返回某个score区间的记录 |
| ZREMRANGEBYSCORE | 移除某个score区间的记录 |
应用场景:
- 排行榜
- 基于score的区间操作
有序集合的不同在于:
Every element in a sorted set is associated with a floating point value, called the score (this is why the type is also similar to a hash, since every element is mapped to a value)
They are ordered according to the following rule:
- If A and B are two elements with a different score, then A > B if A.score is > B.score.
- If A and B have exactly the same score, then A > B if the A string is lexicographically greater than the B string. A and B strings can’t be equal since sorted sets only have unique elements.
内部数据结构实现:包含了skip list和hash table,其插入和更新的时间复杂度为O(log(N))。
Implementation note: Sorted sets are implemented via a dual-ported data structure containing both a skip list and a hash table, so every time we add an element Redis performs an O(log(N)) operation. That’s good, but when we ask for sorted elements Redis does not have to do any work at all, it’s already all sorted.
下面使用ZSET存储历史上的一些计算机名人,会按年龄自动排序。
> zadd hackers 1940 "Alan Kay"
(integer) 1
> zadd hackers 1957 "Sophie Wilson"
(integer) 1
> zadd hackers 1953 "Richard Stallman"
(integer) 1
> zadd hackers 1949 "Anita Borg"
(integer) 1
> zadd hackers 1965 "Yukihiro Matsumoto"
(integer) 1
> zadd hackers 1914 "Hedy Lamarr"
(integer) 1
> zadd hackers 1916 "Claude Shannon"
(integer) 1
> zadd hackers 1969 "Linus Torvalds"
(integer) 1
> zadd hackers 1912 "Alan Turing"
(integer) 1
> zrange hackers 0 -1
1) "Alan Turing"
2) "Hedy Lamarr"
3) "Claude Shannon"
4) "Alan Kay"
5) "Anita Borg"
6) "Richard Stallman"
7) "Sophie Wilson"
8) "Yukihiro Matsumoto"
9) "Linus Torvalds"
> zrevrange hackers 0 -1
1) "Linus Torvalds"
2) "Yukihiro Matsumoto"
3) "Sophie Wilson"
4) "Richard Stallman"
5) "Anita Borg"
6) "Alan Kay"
7) "Claude Shannon"
8) "Hedy Lamarr"
9) "Alan Turing"
Bitmap
| 命令 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| SETBIT | 对某个bit位进行设置 |
| GETBIT | 获取某个bit位的值 |
| BITCOUNT | 返回bit位为1的数量 |
- Bitmap底层使用STRING实现,总共可以记录
2^32个bit(每个bit位上记录0或1),总共占用内存512 MB,使用Bitmap的好处是节省内存。 - 当Bitmap的空间不够时,Redis会自动扩展底层的STRING长度。
- 没有设置的bit位默认为0。
- 例如,用bitmap记录不同的用户ID,可以标识
4亿个不同的用户,且只用了512 MB的内存空间。
Bitmaps are not an actual data type, but a set of bit-oriented operations defined on the String type. Since strings are binary safe blobs and their maximum length is 512 MB, they are suitable to set up to 2^32(= 2^9 * 2^20 * 2^3) different bits.
> setbit key 10 1
(integer) 1
> getbit key 10
(integer) 1
> getbit key 11
(integer) 0
> setbit key 0 1
(integer) 0
> setbit key 100 1
(integer) 0
> bitcount key
(integer) 2
HyperLogLog(HLL)
| 命令 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| PFADD | 统计unique元素 |
| PFCOUNT | 返回PFADD统计的所有元素的个数 |
- HyperLogLog 用于记录一些unique的元素。
- HLL的原理,类似使用SET记录每个元素,并保证唯一,不同的是只是记录状态,而不实际存储元素。
- 应用场景:记录某个场景下的新用户个数。
问题:记录unique元素的功能,对存储空间要求较高。
Usually counting unique items requires using an amount of memory proportional to the number of items you want to count, because you need to remember the elements you have already seen in the past in order to avoid counting them multiple times.
解决方案:
The magic of this algorithm is that you no longer need to use an amount of memory proportional to the number of items counted, and instead can use a constant amount of memory! 12k bytes in the worst case, or a lot less if your HyperLogLog (We’ll just call them HLL from now) has seen very few elements.
> pfadd hll a b c d
(integer) 1
> pfcount hll
(integer) 4
执行命令
进一步了解Redis Command有哪些命令。
Redis的所有命令定义:
void foobarCommand(client *c) {
printf("%s",c->argv[1]->ptr); /* Do something with the argument. */
addReply(c,shared.ok); /* Reply something to the client. */
}
在server.c中定义了command table:
{"foobar",foobarCommand,2,"rtF",0,NULL,0,0,0,0,0},
含义:
- 2:表示此命令的参数个数
- rtF:表示命令的flag
- 命令执行结果通过
addReply()函数返回,在networking.c定义
可以在Redis中扩展和定义自己的命令。
Lua scripts server
It is possible to run Lua scripts server side to improve latency and bandwidth.
https://redis.io/commands/eval
Pub-Sub server
Redis is also a Pub-Sub server.
https://redis.io/topics/pubsub
| 命令 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| subscribe channel [channel …] | 订阅给定的一个或多个频道 |
| unsubscribe [channel [channel …]] | 退订给定的一个或多个频道,如果执行时没有给定任何频道,则退订所有频道 |
| publish channel message | 向指定频道发送消息 |
| psubscribe pattern [pattern …] | 订阅与给定模式相匹配的所有频道 |
| punsubscribe [pattern [pattern …]] | 退订给定的模式,如果没有给定任何模式,则退订所有模式 |
注意:如何使用Redis实现可靠的消息传递?
Redis的事务
Redis有5个命令可以在不被打断的情况下对多个键执行操作。Redis的事务以MULTI命令开始,之后跟着用户传入的多个命令,最后以EXEC结束。这种简单的事务在EXEC命令被调用之前不会执行任何实际操作,所以用户将没办法根据读取到的数据来做决定。
- WATCH
- MULTI
- EXEC
- UNWATCH
- DISCARD
在关系型数据库中,使用select for update是一种悲观锁,持有锁的客户端运行越慢,等待解锁的客户端被阻塞的时间就越长。
Redis的一种事务的处理方法(思想类似,乐观锁):使用WATCH对键进行监视,直到用户尝试执行EXEC命令的这段时间里,如果有其他客户端抢先对任何被监视的键进行了替换,更新或者删除等操作,那么当用户尝试执行EXEC命令的时候,事务将失败并返回一个错误(客户端可以选择重试或者取消)。通过使用WATCH可以保证在执行某些重要操作的时候,确保自己正在用的数据没有发生变化来避免数据出错。
watch
multi
# 操作1
# 操作2
exec
除了通过命令的方式,从Redis 2.6开始也支持Lua脚本的方式支持事务,此方式也更加高效。详见:Redis scripting and transactions
Atomicity of scripts
Redis uses the same Lua interpreter to run all the commands. Also Redis guarantees that a script is executed in an atomic way: no other script or Redis command will be executed while a script is being executed. This semantic is similar to the one of MULTI / EXEC. From the point of view of all the other clients the effects of a script are either still not visible or already completed.
However this also means that executing slow scripts is not a good idea. It is not hard to create fast scripts, as the script overhead is very low, but if you are going to use slow scripts you should be aware that while the script is running no other client can execute commands.
refer:
Redis键的过期时间
在使用Redis存储数据时,有些数据仅在一段很短的时间内有用,虽然可以在数据的有效期过了之后手动删除无用的数据,但更好的办法是使用Redis提供的键过期操作来自动删除无用数据。
- 显示删除
DEL命令
- 自动删除
| 命令 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| PERSIST key-name | 移除键的过期时间 |
| TTL key-name | 查看给定键距离过期还有多少秒 |
| EXPIRE key-name seconds | 让给定键在指定的秒数后过期 |
| EXPIREAT key-name timestamp | 将给定键的过期时间设置为给定的UNIX时间戳 |
| PTTL key-name | 单位是毫秒,Redis2.6以上版本可用 |
| PEXPIRE key-name milliseconds | 单位毫秒 |
| PEXPIREAT key-name timestamp-milliseconds | 单位毫秒 |
Redis的持久化
Redis提供了两种不同的持久化方法。
快照持久化 (允许丢数据)
将存在于某一时刻的所有数据都写入硬盘里。
共享选项,决定快照文件和AOF文件的保存位置。
dir ./
快照持久化配置选项:
save 60 1000
stop-writes-on-bgsave-error no
rdbcompression yes
dbfilename dump.rdb
创建快照的几个方法:
- 客户端发送
BGSAVE命令来创建一个快照。Redis会调用fork创建一个子进程负责将快照写入硬盘,而父进程则继续处理命令请求。 - 客户端发送
SAVE命令来创建一个快照。区别是,Redis在创建快照之前将不再响应任何其他命令。(此命令并不常用) - 如果用户设置了save选项配置,比如,
save 60 1000,那么从Redis最近一次创建快照之后开始算起,当60秒之内有1000次写入这个条件被满足时,Redis就会自动触发BGSAVE命令。如果用户设置了多个save配置选项,那么当任意一个save配置选项所设置的条件被满足时,Redis就会触发一次BGSAVE。 - 当Redis通过
SHUTDOWN命令接收到关闭服务器的请求时,或者收到标准TERM信号时,会执行一个SAVE命令,阻塞所有客户端,不再执行客户端发送的任何命令,并在SAVE命令执行完毕之后关闭服务器。 - 当一个Redis服务器连接另一个Redis服务器,并向对方发送
SYNC命令来开始一次复制操作的时候,如果主服务器没有在执行BGSAVE操作,或者主服务器并非刚刚执行完BGSAVE操作,那么主服务器就会执行BGSAVE。
AOF持久化
只追加文件(Append-Only File),在执行写命令时,将被执行的写命令复制到硬盘里。因此,Redis只要从头到尾重新执行一次AOF文件包含的所有写命令,就可以恢复AOF文件所记录的数据集。
AOF持久化配置选项:
appendonly no
appendfsync everysec/always/no
no-appendsync-on-rewrite no
auto-aof-rewrite-percentage 100
auto-aof-rewrite-min-size 64mb
Redis的复制
复制(replication)可以实现读写分离,作为扩展性能的一种手段。
配置选项:
- 如果在启动Redis服务器指定了
slaveof host port选项配置,那么Redis服务器将根据该选项来连接主服务器。 - 发送
slaveof no one命令让服务器终止复制操作,不再接受主服务器的数据更新。 - 发送
slaveof host port命令让服务器开始复制一个新的主服务器。
Redis的性能
要对Redis的性能进行优化,首先需要知道各种命令的执行速度,可以通过附带的性能测试程序redis-benchmark测试,可以展示一些常用命令在1秒内可以执行的次数。
# -c 1 一个客户端, 不指定则默认为50个客户端
# -q 简化输出结果
redis-benchmark -c 1 -1
refer:
Redis的应用
- 对文章进行投票。例如,StackOverflow是一个可以对问题进行投票的网站